ZnO turns yellow on heating. Why?
ZnO turns yellow on heating.
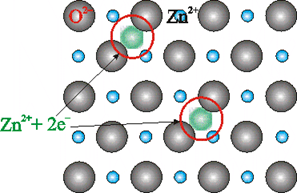
By the presence of extra cations in the interstitial sites: Metal excess may also be caused by an extra cation occupying the interstitial site. Electrical neutrality is maintained by an electron present in another interstitial site.
For example, when ZnO is heated, it loses oxygen and turns yellow due to the following reaction:
![]()
The excess of Zn2+ ions thus formed get trapped into the vacant interstitial sites and electrons in the neighboring interstitial sites.
3