Our solar system consists of 8 planets, dozens of moons, asteroids, comets and meteorites. Have you ever wondered, what is the origin of this vast solar system and ever expanding universe? In this chapter, we will discuss all the aspects of formation and evolution of universe.
Origin of the universe
Big Bang Theory
- It is also called expanding universe hypothesis
- Edwin Hubble provided the evidence of expanding universe.
- The idea of Big Bang theory was first suggested by Georges Lemaitre by taking idea from Hubble’s evidences.
- Stages of development of universe as per the Big Bang theory –
- A tiny ball with an infinitely small volume, infinite temperature and density existed which consisted of all matter forming the universe.
- This tiny ball exploded at the time of Big Bang and the energy was converted into matter.
- Just after the bang, the expansion was very rapid. Thereafter, it has slowed down.
- Within 3,00,000 years from the big bang, temperature dropped to 4500K and gave rise to atomic matter
Hoyle’s concept of steady state
- According to this theory, number of galaxies in the observable universe always remain constant.
- New galaxies are being created out of empty space, which fill up the gaps caused by those galaxies, which have crossed the boundary of observable universe.
Note – With authentic evidences of expanding universe, steady state theory was never accepted by the scientific community.
Pulsating Theory
- This theory laid down that the universe is alternatively expanding and contracting.
- At present, the universe is expanding and at any certain time, this expansion may be stopped by the gravitational pull and the universe will start contracting.
- After it has been contracted to a certain size, explosion again occurs and the universe will start expanding.
ORIGIN OF THE EARTH
Nebular Hypothesis
- It was given by Immanuel Kant. It was revised by Laplace.
- According to this hypothesis, planets were formed out of cloud of material associated with a youthful Sun, which was slowly rotating.
- These clouds are gravitational unstable and matter within them slowly coalesce to smaller denser clumps which slowly collapse and form stars.
Revision of Nebular Hypothesis
- Otto Schmidt and Carl Weizascar again revised the hypothesis.
- According to them, the Sun was surrounded by solar nebula containing Hydrogen and Helium along with dust.
- The friction and collision of particles led to the formation of a disk-shaped cloud and the planets were formed through the process of accretion.
“Accretion” – Cohesion of matter under the influence of gravitation to form larger bodies.
Galaxy
- A galaxy is vast system of group of stars containing a large amount of gas clouds and dust.
- Our Earth is located in spiral shaped Milky Way galaxy.
- First person to see Milky way galaxy was Galileo Galilei
- Andromeda is the galaxy nearest to Milky Way.
Formation of Stars
- A galaxy starts to form by accumulation of hydrogen gas in the form of a dense cloud called Nebula.
- The growing nebula develops localized cluster of gas. These clusters continue to grow into even denser bodies giving rise to the formation of stars.
The Solar System
The sun, eight planets, satellites and some other celestial bodies known as asteroids and meteoroids form the solar system. We often call it a solar family, with the sun as its Head.
The sun
- The centre of the solar system.
- Made up of extremely hot gases. Hydrogen and Helium are the main gases.
- Within the Sun, Hydrogen is converted to Helium by Nuclear Fusion
- Outer layers of Sun’s surface made up of thin hot gases is called Corona. It is visible only during the total solar eclipse.
- The ultimate source of heat and light for the solar system.
- Light takes about 8 minutes from the Sun to reach the Earth
Solar Flares – It is a storm of atoms dissipating from the Sun’s surface and goes into the outer space.
- When solar flares reach Earth’s atmosphere, it collides with dust particles producing colour effect. This effect can be seen as Aurora Borealis in North pole region and Aurora Australis in South-Pole region.
- Region from where the solar flares originate is called Sun Spot.
Planets
There are eight planets in our solar system. They move around the sun in fixed paths. These paths are called orbits. In order of their distance from the sun, they are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
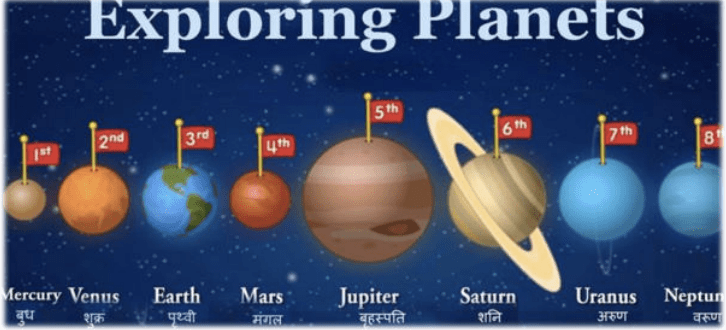
Planets are classified as Terrestrial/Inner planets and Jovian/Outer planets. Mercury,
Venus, Earth and Mars are the terrestrial planets while Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and
Neptune are the Jovian (gaseous) planets.
Mercury
- Closest planet to the sun
- Seen only in morning and evening twilight
- Smallest planetin solar system
- Time taken to orbit the Sun –88 days
- It has no water on it
Venus
- Brightest and Hottest; Also known as morning star or evening star
- Surrounded by a thick cloud cover; hence known as veiled planet known as Earth’s twin as it resembles Earth in shape and size
Earth
- Third closest to sun and fifth largest
- Only planet which sustains life
- Slightly flattened on the poles and has a bulge in the middle
- Due to presence of water; it is known as Blue Planet
- Rotates by 10 in 4 minutes
Mars
- Red planet; due to presence of Iron rich red soil
- It has two moons - Phobos and Deimos
- Atmoshere made of CO2, Nitrogen and Argon
Jupiter
- Largest planet of Solar system
- Winter planet due to low temperature
- Ganymede largest satellite of solar system
Saturn
- Second Largest planet of solar system
- It has bright concentric rings made up of ice and dust
- Titan is the largest satellite of Saturn
Uranus
- Discovered by telescope by Sir William Herschel
- Greenish in colour due to presence of Methane
- Rotates from East to West on its axis
- Surrounded by 13 rings
Neptune
- 8th planet of solar system
- Considered as Uranus’ twins
- Surrounded by methane rings
The Moon
- Our earth has only one satellite, that is, the moon.
- Its diameter is only one-quarter that of the earth
- It has 1/6th gravitational pull of the Earth
- Only 59% of moon’s surface is visible from Earth
- The moon moves around the earth in about 27.5 days.
- Maximum distance between Earth and moon is called Apogee while the minimum distance is called Perigee.
- Highest point on the moon – Mount Leibnitz
Super moon – When full moon comes closest to the Earth, it is called super moon.
Blue moon – If there are two full moons in a calendar month, the second full moon is called Blue moon.
Blood moon – A blood moon is the name given to a view of the moon during a total lunar eclipse.
Study of moon is called Selenology
Moon is also called Fossil planet
The Constellations
A constellation is a group of stars. At present 88 constellations are recognized.
Major constellations given below:
Constellations – Indian Names
- Ursa Major (Great Bear) – Saptarishi
- Cancer – Kark
- Ursa Minor (Little Bear) – Dhruv Matsya
- Leo – Singha
- Orion (Hunter) – Mriga
- Virgo – Kanya
- Oraco (Dragon) – Kaleya
- Sagittarius – Dhanu
- Scorpio – Vrishchika
- Libra – Tula
- Aries – Mesh
- Capricorn – Makar
- Taurus – Vrishchik
- Aquarius – Kumbh
- Gemini – Mithun
- Pisces – Meen
ASTEROIDS
- Many tiny bodies which move around the sun are asteroids
- Mainly composed of mineral and rock
- Found between orbits of Mars and Jupiter
Meteors and Meteorites
- Meteors are formed due to the collision of asteroids with one another. These are also called shooting stars.
- Meteors burn up completely before reaching the surface of Earth. Meteors are known as Meteorites when these are large and do not burn up completely before landing on the surface of Earth.
Comets
- These are the visitors of solar system which move around the sun in regular orbits.
- Comets are made up of frozen gases. A comet is visible when it travels close to the sun.
- It consists of a tail which always points away from the sun.