State of the Economy
India’s GDP growth is expected to remain robust in FY24. GDP forecast for FY24 to be in the range of 6-6.8%. For FY 2022-23, India’s GDP growth will be 7% (Provisional Actuals).
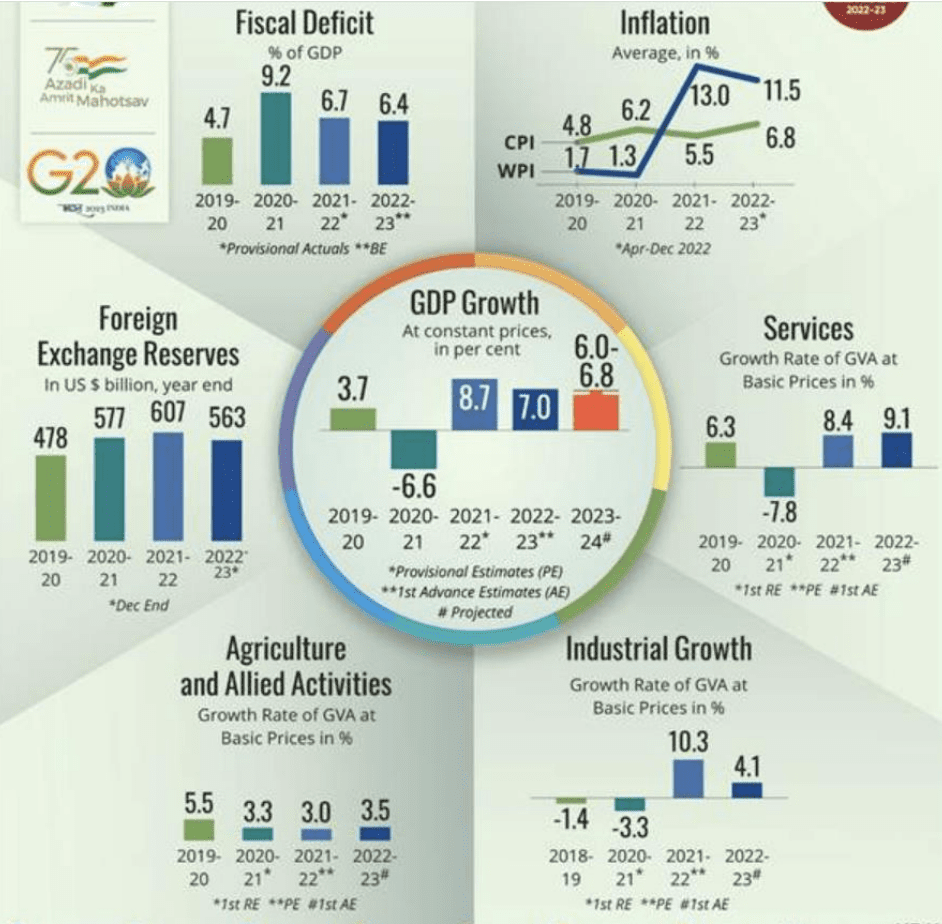
Fiscal Developments
- The Gross Tax Revenue registered a YoY growth of 15.5% from April to November 2022.
- GST has stabilized as a vital revenue source for central and state governments, with the gross GST collections increasing at 24.8% on YoY basis from April to December 2022.
- Capital Expenditure – The Centre’s Capex has steadily increased from a long-term average of 1.7 per cent of GDP (FY09 to FY20) to 2.5 per cent of GDP in FY22 PA.
- It is further budgeted to increase to 2.9% of GDP in FY23
- The Survey informed that ₹7.5 lakh crore of Capital Expenditure is budgeted for FY23, of which more than 59.6 % has been spent from April to November 2022
- Rs.1.5 lakh crore was allocated to road transport and highways, Rs.1.20 lakh crore to railways, 0.7 lakh crore to defence and 0.3 lakh crore to telecommunications in FY22
- Revenue Expenditure – The revenue expenditure of the Union government was brought down from 15.6% of GDP in FY21 to 13.5% of GDP in FY22
- This contraction was led by a reduction of the subsidy expenditure which was brought down from 3.6% of GDP in FY21 to 1.9% of GDP in FY22 PA.
- It was further budgeted to reduce to 1.2% of GDP in FY23
- Direct taxes grew at 26% Year on Year basis due to corporate and personal income tax growth in FY22
- High imports have led to a 12.4% YoY growth in the customs collection from April to November 2022
- Disinvestment – Out of the budgeted amount of ₹65,000 crore for FY23, 48% has been collected as of 18 January 2023
- State finances – The combined Gross Fiscal Deficit of the States, which increased to 4.1% of GDP in FY21, was brought down to 2.8% in FY22 PA. It has been budgeted at 3.4% in FY23
- Debt to GDP ratio – General Government Debt to GDP ratio increased from 75.7% of end- March 2020 to 89.6% at the end of the pandemic year FY21. It is estimated to decline to 84.5% of GDP by end-March 2022
- National Monetization Pipeline – Against the monetization target of ₹0.9 lakh crore in FY22, ₹0.97 lakh crore have been achieved during the period under roads, power, coal and mines.
Monetary Management
- The RBI initiated its monetary tightening cycle in April 2022 and has since raised the repo rate by 225 bps
- The Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio of SCBs has fallen to a seven-year low of 5.0.
- The Capital-to-Risk Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) remains healthy at 16.0.
- The recovery rate for the SCBs through Insolvency and Bankruptcy (IBC) was highest in FY22 compared to other channels.
Inflation and Prices
- While the year 2022 witnessed a return of high inflation in the advanced world after three to four decades, India caps the rise in prices.
- While India’s retail inflation rate peaked at 7.8 per cent in April 2022, above the RBI’s upper tolerance limit of 6 per cent, the overshoot of inflation above the upper end of the target range in India was however one of the lowest in the world.
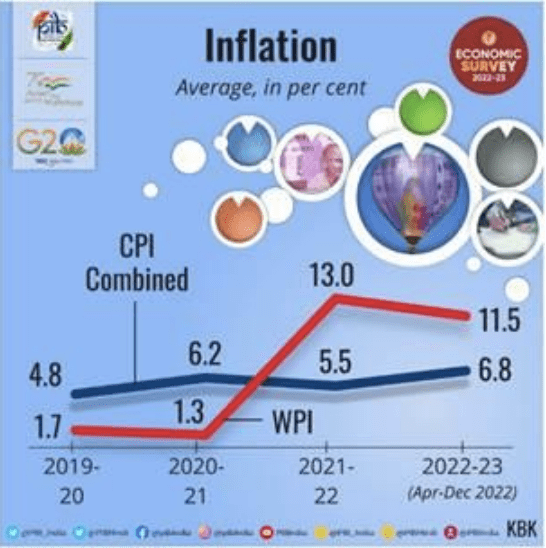
The government adopted a multi-pronged approach to tame the increase in price levels:
- Phase wise reduction in export duty of petrol and diesel
- Import duty on major inputs were brought to zero while tax on export of iron ores and concentrates increased from 30% to 50%
- Waived customs duty on cotton imports w.e.f 14 April 2022, until 30 September 2022
- Prohibition on the export of wheat products under HS Code 1101 and imposition of export duty on rice
- Reduction in basic duty on crude and refined palm oil, crude soyabean oil and crude sunflower oil
Social Sector
- The share of expenditure on social services in the total expenditure of the Government has been around 25% from FY18 to FY20.
- It increased to 26.6% in FY23 (BE)
- The social services expenditure witnessed an increase of 31.4% increase in FY22 over FY21
- The social sector expenditure outlay of the Centre and State governments has increased steadily to stand at 21.3 lakh crore in FY23 (BE). It was 9.15 Lakh crore in FY 16
- The share of expenditure on health in the total expenditure on social services, has increased from 21% in FY19 to 26% in FY23 (BE)
- Survey highlights the findings of the 2022 report of the UNDP on Multidimensional Poverty Index which says that 41.5 crore people exit poverty in India between 2005-06 and 2019-20
Aadhar for Delivery of Social Services
- 318 Central schemes and over 720 state DBT schemes are notified under section 7 of the Aadhaar Act, 2016,
- Various initiatives like Direct Benefit Transfer, Aadhaar Enabled Payment systems, JAM (Jan-Dhan, Aadhaar, and Mobile) trinity, One Nation One Ration Card, CoWin use Aadhaar for targeted delivery of financial services, subsidies, and benefits.
- As per Economic Survey, 135.2 Crore Aadhaar enrollments have been generated, 75.3 crore residents have linked their Aadhaar with ration cards to avail of Ration.
Employment
As of 13 December 2022
- 31 States have pre published the draft rules under the Code on Wages
- 28 States under Industrial Relations Code
- 28 States under Code on Social Security
- 26 States under Occupational Safety Health and Working Conditions Code.
Labour markets have recovered beyond pre-Covid levels, in both urban and rural areas, with unemployment rates falling from 5.8 per cent in 2018-19 to 4.2 per cent in 2020-21
As per Annual Survey of Industries (2019-20)
- The food products industry (11.1 per cent) remained the largest employer, followed by wearing apparel (7.6 per cent), basic metals (7.3 per cent), and motor vehicles, trailers, and semi-trailers (6.5 per cent)
- Tamil Nadu had the largest number of persons engaged in factories (26.6 lakh), followed by Gujarat (20.7 lakh), Maharashtra (20.4 lakh), Uttar Pradesh (11.3 lakh), and Karnataka (10.8 lakh)
In FY23, net average monthly subscribers added under EPFO increased from 8.8 lakh in April-November 2021 to 13.2 lakh in April-November 2022
- The swift rebound of formal sector payroll addition can be attributed to the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY), launched in October 2020
As on 31 December 2022, total over 28.5 crore unorganised workers have been registered on E-Shram portal.
- Female registrations stood at 52.8 per cent of the total and 61.7 per cent of total registrations belonged to the age group 18-40 years
- Uttar Pradesh (29.1 per cent), Bihar (10.0 per cent), and West Bengal (9.0 percent) accounted for nearly half of total registrations
- Agriculture sector workers contributed to 52.4 per cent of the total registrations, followed by domestic and household workers (9.8 per cent), and construction workers (9.1 per cent).
Quality Education for All
- The year FY22 saw improvement in Gross Enrolment Ratios (GER) in schools and improvement in gender parity.
- GER in the primary-enrolment in class I to V as a percentage of the population in age 6 to 10 years - for girls as well as boys have improved in FY22
- Number of Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and Indian Institute of Management (IIMs), respectively stand at 23 and 20 in 2022 against 16 and 13 in 2014.
- The strength of Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs) is 25 in 2022 against 9 in 2014
Health
Health Expenditure – The share of government health expenditure in total health
expenditure has increased from 28.6 per cent in FY14 to 40.6 per cent in FY19
- The share of expenditure on health in the total expenditure on social services has increased from 21 per cent in FY19 to 26 per cent in FY23 (BE)
- Central and State Governments’ budgeted expenditure on the health sector reached 2.1 per cent of GDP in FY23 (BE) and 2.2 per cent in FY22 (RE), against 1.6 per cent in FY21
- Primary healthcare expenditure has increased from 51.1 per cent in FY14 to 55.2 per cent in FY19
COVID Health Facilities – A three-tier arrangement of dedicated Covid-19 health facilities in the country was implemented to reduce the risk of cross-infection to non-Covid patients and to make provision for non-Covid essential health services
- It was emphasised that each district of the country should have at least 1 Pressure Swing Adsorption Oxygen Generation Plant from PM-CARES support at the public health facilities.
- Accordingly, 4,135 PSA plants are being established in the country
Health Infrastructure – There has been a rise in the number of Sub-centres (SCs), Primary Health Centres (PHCs), and Community Health Centres (CHCs) in rural areas.
- Under the Ayushman Bharat programme, 1.5 lakh Health & Wellness Centres (HWCs) have been made operational before 31st December, 2022
- 21.9 crore beneficiaries have been verified under the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri – Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) Scheme
- More than 135 Crore cumulative footfall at AB-Health and wellness centres
COVID Vaccines – As on 6 January 2023, India has been able to administer more than 220 crore Covid vaccine doses across the country.
- 97 per cent of eligible beneficiaries have already received at least one dose of Covid-19 vaccine and around 90 per cent of eligible beneficiaries have received both the doses
- The present administration of more than 220 crore Covid-19 vaccine doses was made possible because of the robust digital infrastructure of Co-WIN
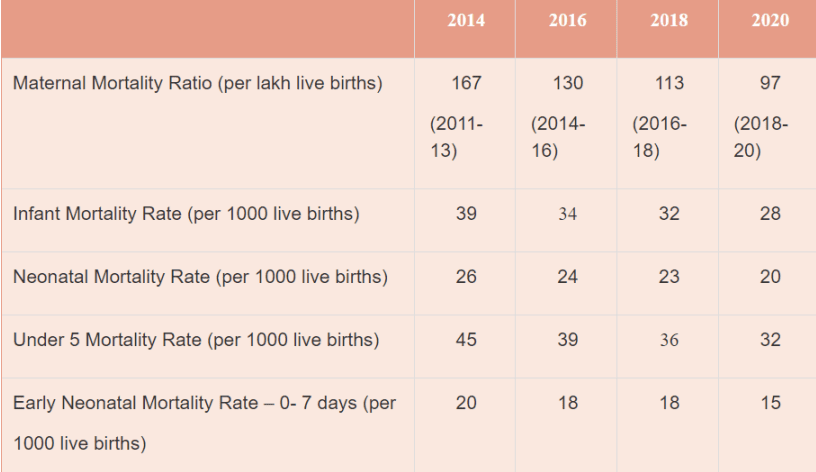
Trends in Mortality Indicators –
Rural Development
65 percent of the country’s population lives in the rural areas and 47 percent of the population is dependent on agriculture for livelihood. The Government’s emphasis has been on improving the quality of life in rural areas to ensure more equitable and inclusive development.
MGNREGA – A total of 5.6 crore households availed employment and a total of 225.8 crore person-days employment has been generated under the MGNREGA (until 6 January 2023)
- The number of works done under MGNREGS has steadily increased over the years, with 85 lakhs completed works in FY22 and 70.6 lakh completed works so far in FY23 (as on 9th Jan 2023)
Housing – A total of 2.7 crore houses have been sanctioned and 2.1 crore houses have been completed by 6 January 2023 under PM Awas Yojana – Gramin
- Against the total target of completion of 52.8 lakh houses in FY23, 32.4 lakh houses have been completed
Water and Sanitation – Since the launch of Jal Jeevan Mission, as of 18 January 2023, of 19.4 crore rural households, 11.0 crore households are getting tap water supply in their homes.
Electricity – Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana, was launched to achieve universal household electrification by providing electricity connections to all willing un-electrified households in rural areas. The scheme has been successfully completed and closed on 31st March 2022.
Smoke Free Rural Homes – The release of 9.5 crore LPG connections under the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana, has helped in increasing the LPG coverage from 62 per cent (on 1 May 2016) to 99.8 per cent (on 1 April 2021)
- Under Ujjwala 2.0 scheme, 1.6 crore connections have been released until 24 November 2022
Women Empowerment – India has around 1.2 crore SHGs, 88 per cent being all-women SHGs. The SHG Bank Linkage Project (SHG-BLP), launched in 1992, has blossomed into the world’s largest microfinance project. SHGs’ bank repayment is more than 96 per cent.
Livelihood and Skill Development – Nearly 4 lakh Self Help Group (SHG) members have been trained as Community Resource Persons (CRPs) help in the implementation of the National Rural Livelihood Mission at the ground level.
Agriculture and Food Management
- India’s agriculture sector has been witnessing robust growth with an average annual growth rate of 4.6 percent over the last six years
- In recent years the country has emerged as the net exporter of agricultural products, with exports in 2021-22 touching a record US $ 50.2 billion
- The Government has set a target of ₹18.5 lakh crores in agricultural credit flow in 2022-23
- The Survey points out that 11.3 crore farmers received income support from the Government under the April-July 2022-23 cycle of PM KISAN.
- The scheme, over the past three years has provided assistance worth more than ₹2 lakh crores to the needy farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojna is currently the largest crop insurance scheme in the world in terms of farmer enrolments, averaging 5.5 crore applications every year and the third largest in terms of the premium received
- India has the highest number of organic farmers in the world at 44.3 lakhs, and 59.1 lakh ha area has been brought under organic farming by 2021-22
- Private investment in agriculture increases to 9.3% in 2020-21.
- Institutional Credit to the Agricultural Sector continued to grow to 18.6 lakh crore in 2021-22
Foodgrains Production – India’s foodgrains production touched a record 315.7 million tonnes in 2021-22. The production of pulses has also been higher than the average of 23.8 million tonnes in the last five years
Animal Husbandry, Dairying and Fisheries
- The livestock sector grew at a CAGR of 7.9 per cent during 2014-15 to 2020-21
- Its contribution to total agriculture GVA (at constant prices) has increased from 24.3 percent in 2014-15 to 30.1 per cent in 2020-21
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana marks the highest-ever investment in the fisheries sector in India was launched with a total outlay of ₹20,050 crore.
- Under a dedicated Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF), proposals to the tune of ₹4,923.9 crore have been approved and have benefitted over 9.4 lakh persons
Food Security
- The Government in a recent decision has decided to provide free foodgrains to about 81.35 crore beneficiaries under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013 for one year from 1st January 2023.
- Further, to remove the financial burden of the poor, the government will spend more than ₹2 lakh crore in this period on food subsidies under NFSA
- Under the PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana, the Government allocated about 1,118 LMT foodgrains to the States/UTs to ease the hardships faced by the poor during the COVID-19 pandemic
Millets
- India produces more than 50.9 million tonnes (as per fourth advance estimate) of millet which accounts for 80 per cent of Asia’s and 20 per cent of global production.
- The global average yield is 1229 kg/ha, whereas India has a higher average yield of 1239 kg/ha
Food Processing Sector
- Over the last five years ending FY21, the food processing industries sector has been growing at an average annual growth rate of around 8.3 per cent
- The value of agri-food exports, including processed food exports, was about 10.9 per cent of India’s total exports during 2021-22
e-NAM
- As on 31 December 2022, more than 1.7 crore farmers and 2.3 lakh traders have been registered on e-NAM portal.
- The scheme was launched to create an online transparent, competitive bidding system to ensure farmers get remunerative prices for their produce
- Under the e-NAM Scheme, the Government provides free software and assistance of ₹75 lakh per APMC mandi for related hardware
Environment
- India’s Forest Cover – India ranks third globally with respect to the net gain in average annual forest area between 2010 and 2020.
- Ramsar Sites - India now has 75 Ramsar sites for wetlands covering the area of 13.3 lakh hectares
- Transition to renewable energy – During the period 2014 -2021, total investment in renewables stood at US$ 78.1 billion in India. The Survey mentions that the likely installed capacity by the end of 2029-30 is expected to be more than 800 GW, of which non-fossil fuel would contribute more than 500 GW. India achieved its target of 40 percent installed electric capacity from non-fossil fuels ahead of 2030. As on 30 September 2022, the government has sanctioned the entire target capacity of 40 GW for the development of 59 Solar Parks in 16 states.
- Green Bonds – The issuance of Sovereign Green Bonds will help the government to tap the requisite finance from potential investors for deployment in public sector projects aimed at reducing the carbon intensity of economy. The Reserve Bank of India has notified the indicative calendar for the issuance of Sovereign Green Bonds for the fiscal year 2022-23, totalling ₹16,000 crore
- National Green Hydrogen Mission to enable India to be energy independent by 2047. Green hydrogen production capacity of at least 5 MMT (Million Metric Tonne) per annum to be developed by 2030
Service Sector
- The services sector witnessed a swift rebound in FY22, growing Year-on-Year (YoY) at 8.4% compared to a contraction of 7.8% in the previous financial year. As per the First Advance Estimates, Gross Value Added (GVA) in the services sector is estimated to grow at 9.1% in FY23,
- India was among the top ten services exporting countries in 2021, with its share in world commercial services exports increasing from 3 per cent in 2015 to 4 per cent in 2021
- Credit to services sector has grown by over 16% since July 2022
- Bank Credit – The bank credit to Services Sector saw a YoY growth of 21.3% in November 2022
- Services exports – It registered growth of 27.7% during April-December 2022 as compared to 20.4% in the corresponding period last year
- FDI in services – India received the highest-ever FDI inflows of US$ 84.8 billion including US$ 7.1 billion FDI equity inflows in the services sector in FY22
- IT-BPM revenues registered YoY growth of 15.5% during FY22 compared to 2.1% growth in FY21. Within the ITBPM sector, IT services constitute the majority share.
- E-commerce – According to the Global Payments Report by Worldpay FIS, India’s e- commerce market is projected to post impressive gains and grow at 18% annually through 2025
- Digital Financial Services – India took the lead with the fintech adoption rate of 87%, substantially higher than the world average of 64% as per the latest Global FinTech Adoption Index
- Real Estate – Sustained growth in the real estate sector is taking housing sales to pre-pandemic levels, with a 50% rise between 2021 and 2022
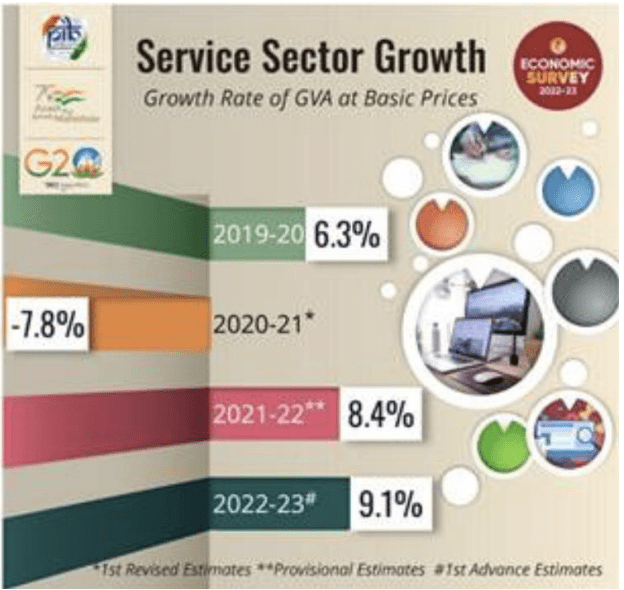
“The Survey noted that India’s services sector growth which was highly volatile and fragile during the last 2 fiscal years, has shown resilience in FY23”
Industry
- Overall Gross Value Added (GVA) by the Industrial Sector (for the first half of FY 22-23) rose 3.7 per cent, which is higher than the average growth of 2.8 per cent achieved in the first half of the last decade
- Credit to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) has grown by an average of around 30% since January 2022 and credit to large industry has been showing double-digit growth since October 2022
- Electronics exports rise nearly threefold, from US $4.4 billion in FY19 to US $11.6 Billion in FY22
- India has become the second-largest mobile phone manufacturer globally, with the production of handsets going up from 6 crore units in FY15 to 29 crore units in FY21
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows into the Pharma Industry has risen four times, from US $180 million in FY19 to US $699 million in FY22
- The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes introduced across 14 categories, with an estimated capex of ₹4 lakh crore over the next five years, to plug India into global supply chains
External Sector
- India achieved an all-time high annual merchandise export of US$ 422 billion in FY’22.
- Merchandise export were US$ 332 billion over April-December 2022 against US$ 305 billion during the period April-December 2021
- India diversified its markets and increased its exports to Brazil, South Africa and Saudi Arabia
- India is the largest recipient of remittances in the world receiving US$ 100 bn in 2022. Remittances are the second largest major source of external financing after service export
- As of December 2022, Forex Reserves stood at US$ 563 bn covering 9.3 months of imports
- As of end-November 2022, India is the sixth largest foreign exchange reserves holder in the world.
- The current stock of external debt is well shielded by the comfortable level of foreign exchange reserves
Transportation and Logistics
- Rapid increase in National Highways (NHs) /Roads Construction with 10457 km NHs/roads constructed in FY22 compared to 6061 km in FY16
- 2359 Kisan rails transported approximately 7.91 lakh tonnes of perishables, as of October 2022
- More than one crore air passengers availed the benefit of the UDAN scheme since its inception in 2016
- Near doubling of capacity of major ports in 8 years
- Inland Vessels Act 2021 replaced 100-year-old Act to ensure hassle free movement of Vessels promoting Inland Water Transport