Introduction
The Union Budget 2023-24 is the first budget of Amrit Kaal.
Visions of Amrit Kaal
- Opportunities for citizens with focus on the youth
- Growth and job creation
- Strong and stable macro-economic environment
Priorities of Budget 2023-24
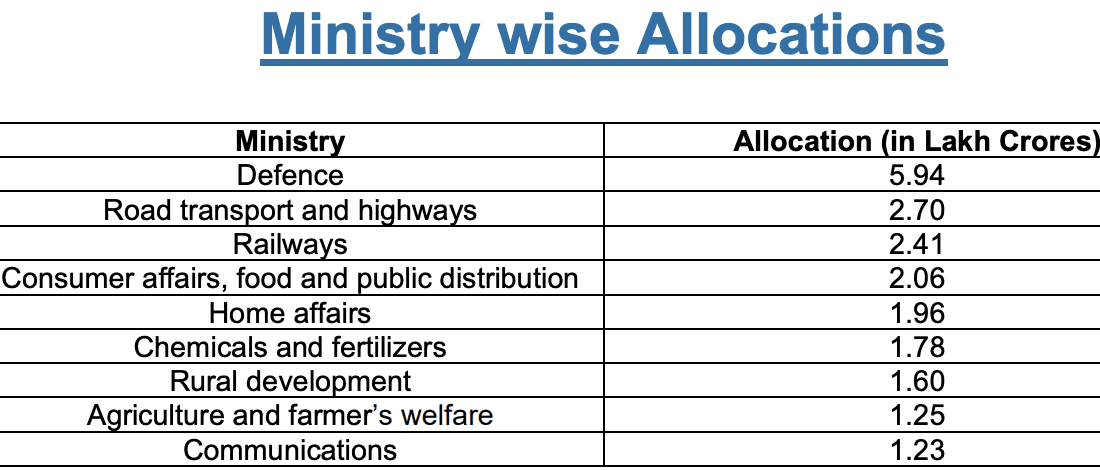
The budget adopts the seven priorities which complement each other and act as the ‘Saptarishi’ guiding us through the Amrit Kaal –
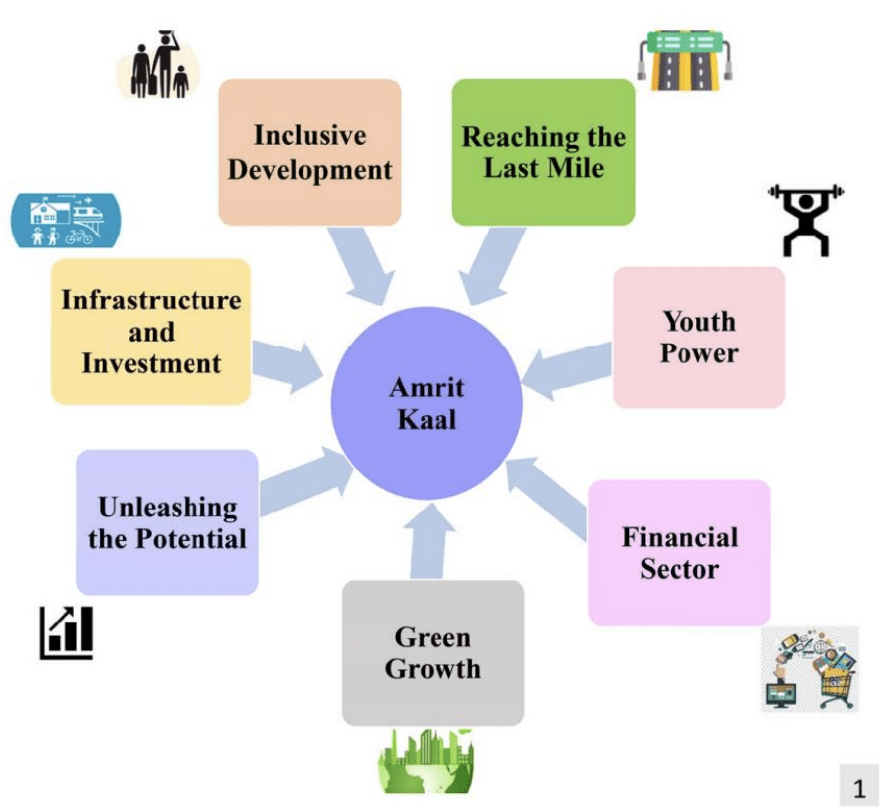
Deficit Statistics
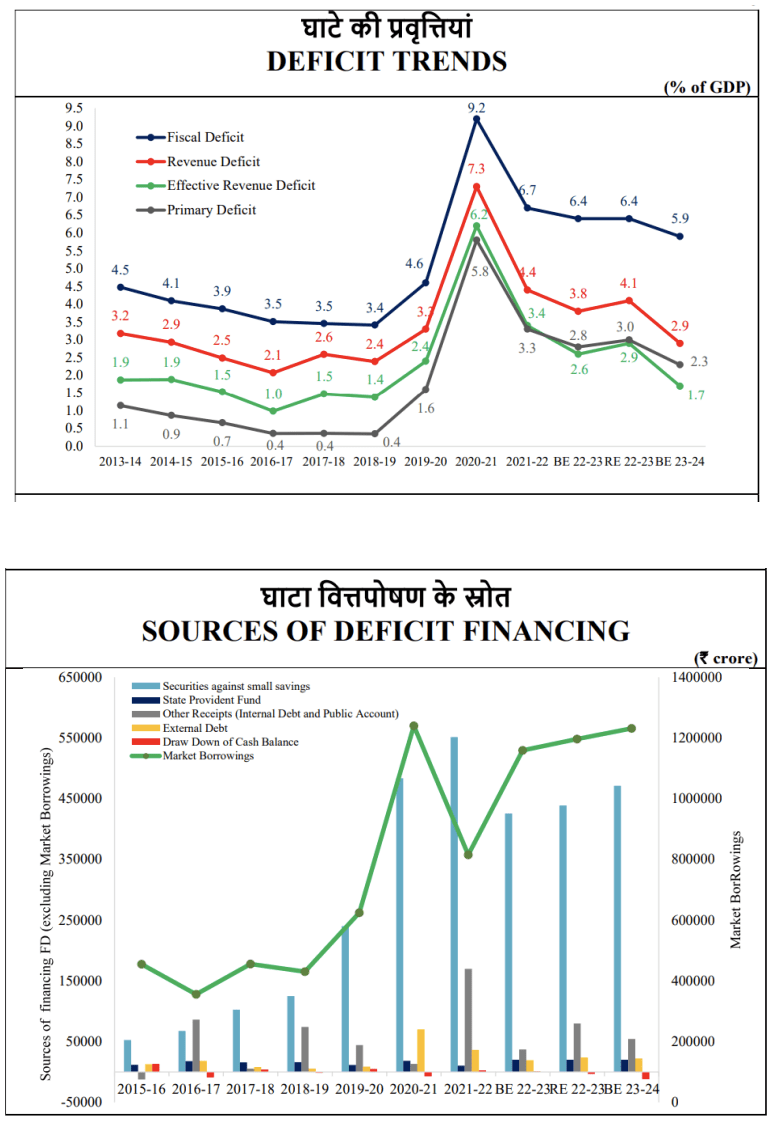
Budgetary Estimates
• Total expenditure – Rs.45.03 Lakh Crores (4503097 Lakh Crores)
• Revenue receipts – Rs.26.32 Lakh Crores
• Capital receipts – Rs.18.70 Lakh Crores
• Capital Expenditure – Rs.10 Lakh Crores
• Revenue Expenditure – Rs.35 Lakh Crores
Schemes Announced
Agriculture Accelerator Fund
• An Agriculture Accelerator Fund will be set-up to encourage agri-startups by young entrepreneurs in rural areas.
• The Fund will aim at bringing innovative and affordable solutions for challenges faced by farmers
Aatmanirbhar Horticulture Clean Plant Program
• This program will be launched to boost availability of disease-free, quality planting material for high value horticultural crops
• Total outlay – Rs.2200 Crores
New Sub-Scheme of PM Matsya Sampada Yojana
• A new sub-scheme of PM Matsya Sampada Yojana with targeted investment of Rs.6,000 crore will be launched
• The sub-scheme will further enable activities of fishermen, fish vendors, and micro & small enterprises, improve value chain efficiencies, and expand the market
National Mission to Eliminate Sickle Cell Anaemia
• The mission will strive to eliminate sickle cell anaemia from the country by 2047
• It will entail awareness creation, universal screening of 7 crore people in the age group of 0-40 years in affected tribal areas, and counselling through collaborative efforts of central ministries and state governments
Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission
• To improve socio-economic conditions of the particularly vulnerable tribal groups
(PVTGs), Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission will be launched
• Under the mission, government will provide basic facilities such as safe housing, clean drinking water and sanitation, improved access to education, health and nutrition, road and telecom connectivity, and sustainable livelihood opportunities to PVTGs
• Total outlay – Rs.15000 Crore
PM Awas Yojana – Enhanced Outlay
• The outlay for PM Awas Yojana is being enhanced by 66 per cent to over Rs.79,000 crore Bharat Shared Repository of Inscriptions (Bharat SHRI)
• Bharat Shared Repository of Inscriptions will be set up in a digital epigraphy museum, with digitization of one lakh ancient inscriptions in the first stage
Urban Infrastructure Development Fund
• An Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF) will be established through use of priority sector lending shortfall
• This will be managed by the National Housing Bank
• It will be used by public agencies to create urban infrastructure in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities
• States will be encouraged to leverage resources from the grants of the 15th Finance Commission, as well as existing schemes, to adopt appropriate user charges
Centres of Excellence of AI
• Three centres of excellence for Artificial Intelligence will be set-up in top educational institutions for realizing the vision of “Make AI in India and Make AI work for India”
• Leading industry players will partner in conducting interdisciplinary research, develop cutting-edge applications and scalable problem solutions in the areas of agriculture, health, and sustainable cities
Vivad se Vishwas – I (Relief for MSMEs)
• In cases of failure by MSMEs to execute contracts during the Covid period, 95 per cent of the forfeited amount relating to bid or performance security, will be returned to them by government and government undertakings
Vivad se Vishwas – II (Settling Contractual Disputes)
• A voluntary settlement scheme with standardized terms will be introduced to settle contractual disputes of government and government undertakings
Phase 3 of e-Courts Project
• The phase 3 of e-courts project will be launched with an outlay of Rs.7000 Crore
Green Credit Program
• A Green Credit Programme will be notified under the Environment (Protection) Act for encouraging behavioral change.
• It will incentivize environmentally sustainable and responsive actions by companies, individuals and local bodies, and help mobilize additional resources for such activities
PM PRANAM
• “PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness, Nourishment and Amelioration of Mother Earth” (PM PRANAM) will be launched.
• To incentivize States and Union Territories to promote alternative fertilizers and balanced use of chemical fertilizers
GOBARdhan Scheme
• 500 new ‘waste to wealth’ plants under GOBARdhan (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan) scheme will be established
• These will include 200 compressed biogas (CBG) plants, including 75 plants in urban areas, and 300 community or cluster-based plants
• The total investment will be Rs.10000 Crore
MISHTI
• “Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes” (MISHTI) will be launched
• It will be launched for mangrove plantation along the coastline and on salt pan lands, wherever feasible, through convergence between MGNREGS, CAMPA Fund and other sources.
Amrit Dharohar
• This scheme will be implemented over the next three years to encourage optimal use of wetlands, and enhance bio-diversity, carbon stock, eco-tourism opportunities and income generation for local communities
PM Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0
• Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 will be launched to skill lakhs of youth within the next three years
• The scheme will also cover new age courses for Industry 4.0 like coding, AI, robotics, mechatronics, IOT, 3D printing, drones, and soft skills
Mahila Samman Bachat Patra
• A one-time new small savings scheme, Mahila Samman Savings Certificate, will be launched
• It will be launched for a two-year period up to March 2025
• The scheme will offer deposit facility up to Rs.2 lakh in the name of women or girls for a tenor of 2 years at fixed interest rate of 7.5 per cent with partial withdrawal option
Senior Citizens Savings Scheme
• The maximum deposit limit for Senior Citizen Savings Scheme will be enhanced from Rs.15 lakh to Rs.30 lakh
Sector Wise Key Announcements
Agriculture and Cooperation
• Digital public infrastructure for agriculture will be built as an open source, open standard and inter operable public good.
▪ This will enable inclusive, farmer-centric solutions through relevant information services for crop planning and health, improved access to farm inputs, credit, and insurance
• A cluster-based and value chain approach through Public Private Partnerships will be adopted to enhance the productivity of extra-long staple cotton
• Global Hub for Millets (Shree Anna)
▪ The Indian Institute of Millet Research, Hyderabad will be supported as the Centre of Excellence for sharing best practices, research and technologies at the international level to make India a global hub for millets
• The agriculture credit target will be increased to Rs.20 lakh crore with focus on animal husbandry, dairy and fisheries
• Bhartiya Prakritik Kheti Bio Input Resources Centre
▪ 10,000 Bio-Input Resource Centres will be set-up
▪ This will facilitate 1 crore farmers to adopt natural farming
Health, Education and Skilling
• 157 new nursing colleges will be established in co-location with the existing 157 medical colleges established since 2014
• A new programme to promote research and innovation in pharmaceuticals will be taken up through centers of excellence
• National Digital Library for children and adolescents will be set-up for facilitating availability of quality books across geographies, languages, genres and levels
• In the next three years, centre will recruit 38,800 teachers and support staff for the 740
Eklavya Model Residential Schools
• Skill India Digital platform will be launched for –
▪ Enabling demand-based formal skilling
▪ Linking with employers including MSMEs
▪ Facilitating access to entrepreneurship schemes
• To provide stipend support to 47 lakh youth in three years, Direct Benefit Transfer under a pan-India National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme will be rolled out
Infrastructure and Investment
• Capital investment outlay will be increased by 33% to Rs.10 lakh crore. This would be 3.3% of GDP
• The ‘Effective Capital Expenditure’ (including Grants in Aid to states) of the Centre is budgeted at Rs.13.7 lakh crore, which will be 4.5 per cent of GDP
• The 50-year interest free loan to state governments will be continued for one more year to spur investment in infrastructure with an enhanced outlay of Rs.1.3 Lakh Crores
• A capital outlay of Rs.2.40 lakh crore has been provided for the Railways
• 100 critical transport infrastructure projects, for last and first mile connectivity for ports, coal, steel, fertilizer, and food grains sectors have been identified
▪ Investment of Rs.75000 crore will be done
• Fifty additional airports, heliports, water aerodromes and advance landing grounds will be revived for improving regional air connectivity
Environment
• Rs.35,000 crore for priority capital investments towards energy transition and net zero objectives, and energy security
• The Inter-state transmission system for evacuation and grid integration of 13 GW renewable energy from Ladakh will be constructed.
▪ Total Investment of Rs.20,700 crore including central support of Rs.8,300 crore is expected
• States will be supported in replacing old vehicles and ambulances under Vehicle scrapping policy
Finance and Banking
• Credit guarantee scheme for MSMEs will be revamped from 1st April 2023 through infusion of Rs.9,000 crore in the corpus. This will enable additional collateral-free guaranteed credit of Rs.2 lakh crore
• National Financial Information Registry – It will be set up to serve as the central repository of financial and ancillary information
• GIFT-IFSC - To enhance business activities in GIFT IFSC, the following measures will be taken:
▪ Delegating powers under the SEZ Act to IFSCA to avoid dual regulation
▪ Setting up a single window IT system for registration and approval from IFSCA, SEZ
authorities, GSTN, RBI, SEBI and IRDAI
▪ Permitting acquisition financing by IFSC Banking Units of foreign banks
▪ Establishing a subsidiary of EXIM Bank for trade re-financing
• For countries looking for digital continuity solutions, Data Embassies will be set up in GIFT IFSC
Taxes and Duties
• Excise duty on GST-paid compressed bio gas will be exempted
• Relief in customs duty on import of certain parts and inputs like camera lens
• Basic customs duty on parts of open cells of TV panels will be reduced to 2.5 per cent
• National Calamity Contingent Duty be revised upwards by about 16 per cent
• Micro enterprises with turnover up to Rs.3 crore and certain professionals with turnover of up to Rs.75 lakh (whose cash receipts are no more than 5 per cent) can avail the benefit of presumptive taxation
• New co-operatives that commence manufacturing activities till 31.3.2024 shall get the benefit of a lower tax rate of 15 per cent
• A higher limit of Rs.3 crore for TDS on cash withdrawal is being provided to co-operative societies
• The date of incorporation for income tax benefits to start-ups will be extended from 31.03.23 to 31.3.24
• Reducing the TDS rate from 30 per cent to 20 per cent on taxable portion of EPF withdrawal in non-PAN cases
Personal Income Tax
• The rebate limit has been increased to Rs.7 Lakhs in the new tax regime
• New income tax slab has been introduced –
Rs. 0-3 lakh : Nil
Rs. 3-6 lakh : 5 per cent
Rs. 6-9 lakh : 10 per cent
Rs. 9-12 lakh : 15 per cent
Rs. 12-15 lakh : 20 per cent
Above Rs.15 lakh : 30 per cent
• Standard deduction for salaried person having income of Rs.15.5 Lakh or more will have standard deduction of Rs.52,500
• The highest surcharge rate will be reduced from 37 per cent to 25 per cent in the new tax regime
• Tax exemption on leave encashment on retirement of non-government salaried employees has been increased to Rs.25 Lakhs
Other Major Announcements
• In the drought prone central region of Karnataka, central assistance of Rs.5,300 crore will be given to Upper Bhadra Project
▪ To provide sustainable micro irrigation and filling up of surface tanks for drinking water
• National Data Governance Policy will be brought out to unleash innovation and research by start-ups and academia
• The financing of select schemes will be changed, on a pilot basis, from ‘input-based’ to ‘result-based’
• Entity Digilocker – It will be set up for use by MSMEs, large business and charitable trusts. This will enable them to store and share online securely, whenever needed, with various authorities, regulators, banks and other business entities
• One hundred labs for developing applications using 5G services will be set up
• Unity Mall – Unity malls will be set up in state capitals or most prominent tourism centre or the financial capital for promotion and sale of states’ own ODOPs, GI products and other handicraft products
• States will be allowed a fiscal deficit of 3.5 per cent of GSDP of which 0.5 per cent will be tied to power sector reforms.
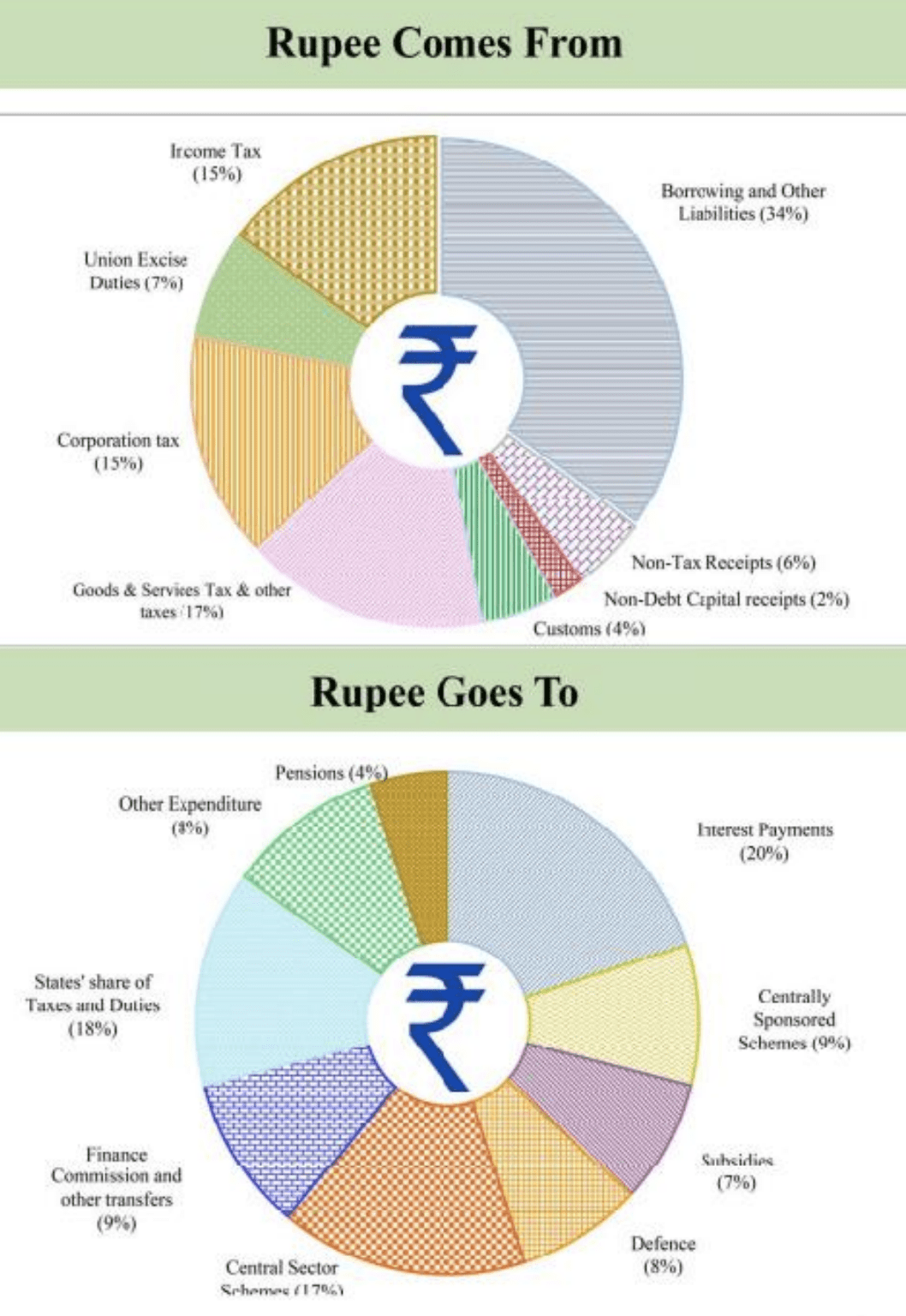
Budgetary Allocation to Important Schemes