Reduce each of the following equations to normal form :
(i) x + y - 2 = 0
(ii) ![]()
(iii) x + 5 = 0
(iv) 2y – 3 =0
(v) 4x + 3y - 9 = 0
![]()
If the equation is in the form of ax + by = c, to get into the normal form we should divide it by ![]() , so now
, so now
Divide by ![]() =
= ![]()
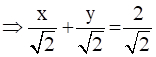

This is in the form of ![]() , where
, where 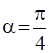 and
and ![]()
Conclusion: 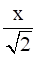 +
+ 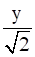 =
= ![]() is the normal form of x + y - 2 = 0
is the normal form of x + y - 2 = 0
(ii) ![]()
⇒x + y = - √2
If the equation is in the form of ax + by = c, to get into the normal form, we should divide it by![]() , so now
, so now
Divide by ![]()
Our new equation is 
This is in the form of ![]() , where
, where 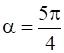 and p =1
and p =1
Conclusion: 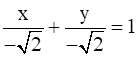 is the normal form of
is the normal form of ![]()
(iii) ![]()
If the equation is in the form of ax + by = c, to get into the normal form, we should divide it by![]() , so now
, so now
Divide the equation by ![]()
Our new equation is ![]()
This is in the form of ![]() , where
, where ![]() and p = 5
and p = 5
Conclusion: ![]() is the normal form of
is the normal form of ![]()
(iv) ![]()
If the equation is in the form of ax + by = c, to get into the normal form, we should divide it by![]() , so now
, so now
Divide by ![]()
Our new equation is 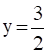
This is in the form of ![]() , where
, where 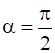 and
and 
Conclusion:  is the normal form of
is the normal form of ![]()
(v) ![]()
If the equation is in the form of ax + by = c, to get into the normal form, we should divide it by ![]() , so now
, so now
Divide by ![]()
Our new equation is 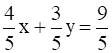
This is in the form of ![]() , where
, where
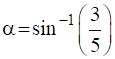 or
or 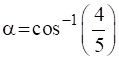 and
and 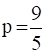
Conclusion: 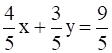 is the normal form of
is the normal form of ![]()