Figure shows a vessel partitioned by a fixed diathermic separator. Different ideal gases are filled in the two parts. The rms speed of the molecules in the left part equals the mean speed of the molecules in the right part. Calculate the ratio of the mass of a molecule in the left part to the mass of a molecule in the right part.

In kinetic theory of ideal gas, the average energy is given by
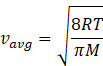
Where R=gas constant=8.31Jmol-1K-1
T=temperature of gas
M=molar mass of gas
We know that,
Gas constant R=kBNA
Where kB= Boltzmann constant = 1.38 × 10–23 J K–1.
NA=Avogadro number=6.023![]() 10-23 mol-1
10-23 mol-1
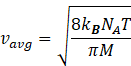
Molar mass of gas molecule M= Avogadro number![]() mass of gas molecule
mass of gas molecule
M=NA![]() m
m ![]()
So average velocity becomes
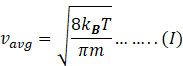
Rms speed of gas molecule is given by

Where R=gas constant 8.31J/molK
T=temperature of gas
M=molar mass of gas
Putting the value gas constant R=kBNA
So rms speed becomes
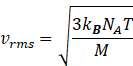
M=NA![]() m
m ![]()
Therefore,

Let the mass of molecule in left part=m1
Mass of molecule in right part=m2
According to question, the rms speed of the molecules in the left part equals the mean speed of the molecules in the right part.
So, from equation (I) and(II) we get
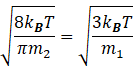
Since the walls of separator is diathermic therefore temperature of both the parts will be same.
Squaring the above equation, we get
![]()
![]()
![]() The ratio of the mass of a molecule in the left part to the mass of a molecule in the right part is 1.17.
The ratio of the mass of a molecule in the left part to the mass of a molecule in the right part is 1.17.