Explain the process of transcription in Prokaryotes.
OR
How does comparative anatomy and morphology act as an evidence for Evolution? Explain with the help of suitable examples.
Transcription: is the process of the formation of the m-RNA strand on a DNA strand in the nucleus.It takes place in three steps:
1. Initiation
2. Elongation
3. Termination
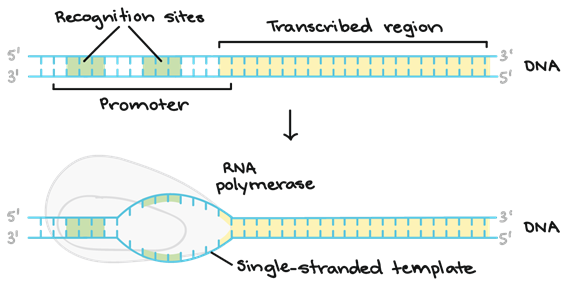
• The enzyme involved in transcription is RNA polymerase, it can initiate transcription by itself.
Steps of Transcription:
1. Initiation:
• A single DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyses transcription of all three types of RNA(mRNA,tRNA and rRNA).
• RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region and starts the process of transcription. The RNA polymerase contains a detachable subunit called Sigmafactor, it helps the enzyme to bind firmly to DNA.
• The RNA core polymerase(minus sigma factor) moves down DNA at a faster pace and this continues to synthesise a new RNA chain.
2. Elongation:
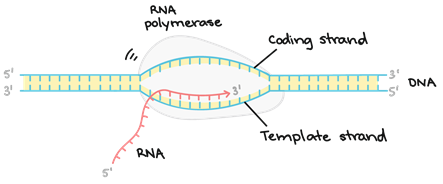
• After synthesis of RNA more than 10bp long, the sigma factor is ejected and the enzyme move along 5’-3’ direction continuously synthesising RNA.
3. Termination
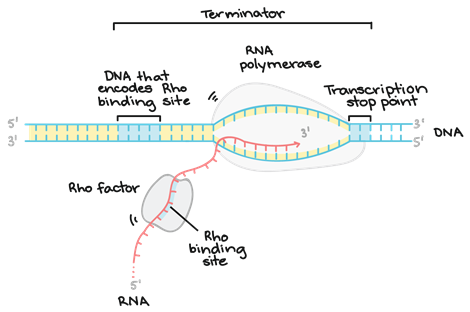
• The process of elongation during transcription continues until the enzyme, RNA core polymerase reaches the terminator sequence in the sense DNA strand (3’-AAAAAAT-5’). At this point another portion particle, the tho factor, forms a complex with RNA-polymerase .This causes the enzyme to go off the DNA track and thus, the mRNA is released.
OR
Comparative anatomy and morphological evidences shows the similarities and differences among the organism of today and those tat existed years ago.
The evidences are as follows:
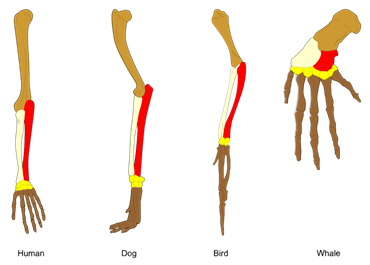
1. Homologous Organs:
• The organs whose structure is same but has different function are called homologous.
• example: forelimbs of animals like Whale, bats and cheetah have similar anatomical structure
• Other example is vertebrates heart or brain.
• Homology is based on divergent evolution. The same structure developed along different directions due to adaptation to different needs.
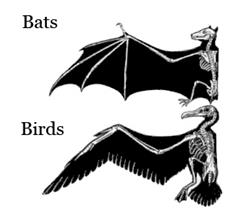
2. Analogous organs
• Organs which have different structure but perform same function is called analogous organs.
• example: wings of butterfly and birds.
• Analogy refers to situation , exactly opposite to homology
• Analogous organs are the result of Convergent evolution. It is the evolution in which different structures evolve for same function.
• Other example: eyes of octopus and mammals, flippers of penguin and dolphins.
3. Vestigial organ
• These are degenerate, non-functional organs.
• There are about 90 vestigial organs in the human body.
• example: human appendix is vestigial in man but functional in rodents, horse and other herbivorous animals.