Explain initiation, elongation and termination in the process of transcription in bacteria.
The process of transcription occurs in 3 major steps:
a. Initiation:The RNA polymerase along with the initiation factor (denoted by sigma, σ) binds to the promoter sequence in DNA. This helps in the opening the DNA helix and separates the two DNA strands. Bacterial RNA polymerase is the principle enzyme involved in transcription.
b. Elongation:During this stage, the RNA polymerase builds a strand of RNA using one of the DNA strands as a template. This RNA chain growth takes place in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Once the chain elongation commences, the sigma factor dissociates from the RNA polymerase which can be reused.
c. Termination: During termination, the polymerase along with the termination-factor, represented by rho (ρ) reaches the terminator region and the newly created mRNA falls off along with the enzyme.
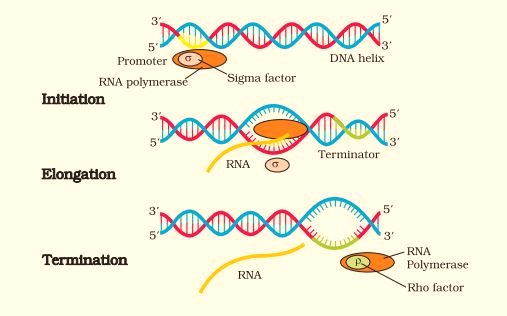
Figure1. Process of transcription in Prokaryotes.