Prove that the opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.
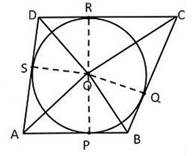
Given: ABCD is a quadrilateral and it has circumscribing a circle with centre O.
To Prove: Opposite sides subtend supplementary angles at the centre
i.e. ∠AOB + ∠COD = 180°
& ∠AOD + ∠BOC = 180°
Let ABCD be a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle with O such that it touches the circle at point P, Q, R, S.
Construction: Join OP, OQ, OR and OS
Proof:
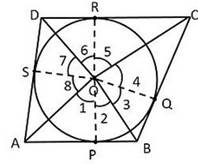
In ΔOAP and ΔOAS,
AP = AS
[Length of tangents drawn from external point to a circle are equal]
OP = OS [Radii of the circle]
OA = OA [Common side]
∴ ΔOAP ≅ ΔOAS [SSS congruence rule]
∴ ∠POA = ∠AOS [By CPCT]
⇒ ∠1 = ∠8 …(i)
Similarly we get,
∠2 = ∠3 …(ii)
∠4 = ∠5 …(iii)
∠6 = ∠7 …(iv)
Adding all these angles,
∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠4 + ∠5 + ∠6 + ∠7 +∠8 = 360°
[Sum of angles round a point is 360°]
⇒ (∠1 + ∠8) + (∠2 + ∠3) + (∠4 + ∠5) + (∠6 + ∠7) = 360°
⇒ (∠1 + ∠1) + (∠2 + ∠2) + (∠5 + ∠5) + (∠6 + ∠6) = 360°
[from (i), (ii), (iii) & (iv)]
⇒ 2 (∠1) + 2 (∠2) + 2 (∠5) + 2 (∠6) = 360°
⇒ 2(∠1 + ∠2) + 2(∠5 + ∠6) = 360°
⇒ (∠1 + ∠2) + (∠5 + ∠6) = 180°
⇒ ∠AOB + ∠COD = 180°
Hence, both angle are supplementary
Similarly, we can prove that ∠ BOC + ∠ DOA = 180°
Adding all these angles,
∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠4 + ∠5 + ∠6 + ∠7 +∠8 = 360°
[Sum of angles round a point is 360°]
⇒ (∠1 + ∠8) + (∠2 + ∠3) + (∠4 + ∠5) + (∠6 + ∠7) = 360°
⇒ (∠8 + ∠8) + (∠3 + ∠3) + (∠4 + ∠4) + (∠7 + ∠7) = 360°
[from (i), (ii), (iii) & (iv)]
⇒ 2 (∠8) + 2 (∠3) + 2 (∠4) + 2 (∠7) = 360°
⇒ 2(∠7+ ∠8) + 2(∠3 + ∠4) = 360°
⇒ (∠7+ ∠8) + (∠3 + ∠4) = 180°
⇒ ∠AOD + ∠BOC = 180°
Hence, both angle are supplementary
Hence, opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.