Describe the asexual and sexual phases of life cycle of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans.
OR
(a) What is plant breeding? List the two steps the classical plant breeding involves.
(b) How has the mutation breeding helped in improving crop varieties? Give one example where this technique has helped.
(c) How has the breeding programmed helped in improving the public nutritional health? State two examples in support of your answer.
Life Cycle of Plasmodium :
1. Plasmodium parasite requires two hosts to complete its life cycle.
2. When female Anopheles mosquito bites a healthy human being, it injects Plasmodium, which lives in its Anopheles mosquito as sporozoite the infectious form.
3. The parasites Plasmodium reaches the liver through blood where they multiply asexually and finally rupture the liver cells. Sporozoites parasite are then released into blood-stream.
4. Bursting of RBCs is occur due to the release of a toxic substance called haemozoin (associated with fever and chills).
5. In the RBCs, only sporozoites undergo sexual stages (gametocytes).
6. When the diseased person is bitten by a female Anopheles mosquito, gametocytes are introduced into the mosquito.
7. Gametocytes fertilization and development takes place in the gut of mosquito to form sporozoites.
8. Sporozoites are stored in the salivary glands of mosquito and are released into the healthy person who is bitten by this mosquito.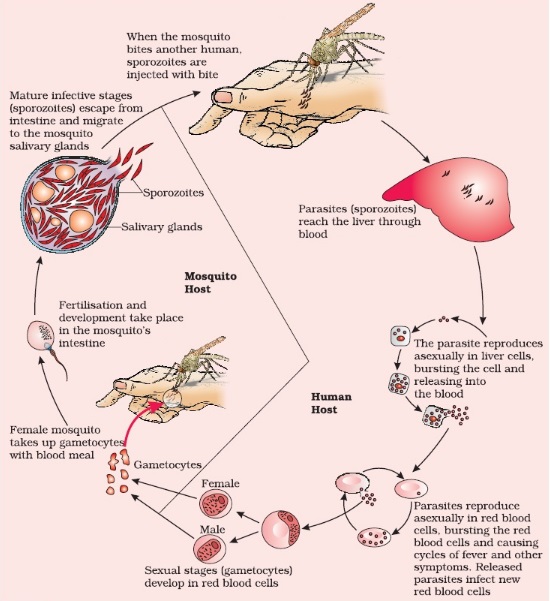
OR
(a) Plant breeding is the purposely manipulation of plant species in which the crossing of two plants to develop the desired plant types that are better suited for cultivation, give better yields, and are disease resistant.
Two steps involved in Classical plant breeding are :
1. Crossing of superior pure lines and
2. Selection of plants with desired characteristics.
(b)Mutation breeding: In this, genetic variations are made, which then creates traits, not found in the parental type. It has benefited in making disease-resistant plants by giving resistance against bacterial, fungal and viral diseases and high yield also. Resistance to a yellow mosaic virus in bhindi (Abelmoschusesculentus) was transferred from a wild species and resulted in a new variety called Parbhanikranti.
(c) Bio-fortification is breeding crops helped in improvising the public nutritional health by growing crops that are good in nutrients. Benefits of bio-fortification are to help :
1. Protein content and quality
2. Oil content and quality
3. Vitamin content
4. Micronutrient and mineral content Two examples are :
(i) Maize hybrids grows in 2000 and have 2 times the quantity of lysine and tryptophan compared to other maize hybrids.
(ii) Atlas 66 (a wheat variety having higher protein content).