How is the amplification of a gene sample of interest carried out using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
Polymerase chain reaction is a method widely used in molecular biology to make many copies of a specific DNA segment. The steps involved are:
a. Denaturation: The double-stranded DNA is denatured by applying high temperature of 95°C for 15 seconds. Each separated single strand now acts as template for DNA synthesis.
b. Annealing: Two sets of primers are added which anneal to the 3′ end of each separated strand. Primers act as initiators of replication.
c. Extension: DNA polymerase extends the primers by adding nucleotides complementary to the template provided in the reaction. Taq polymerase, thermostable DNA polymerase, is used in the reaction.
All these steps are repeated many times to obtain several copies of desired DNA.
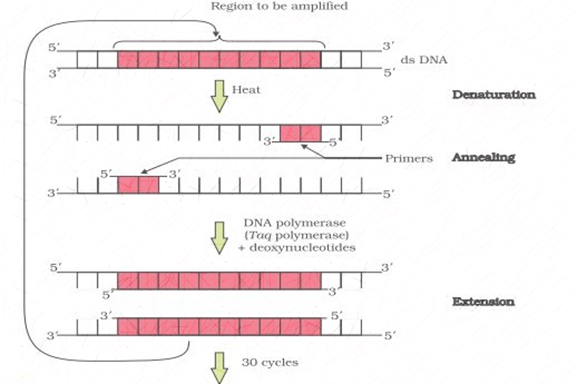
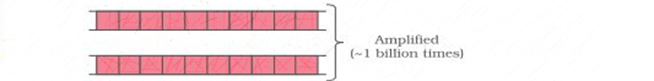
Figure 2. Steps involved in PCR.