Describe Frederick Griffith’s experiment on Streptococcus pneumoniae. Discuss the conclusion he arrived at.
OR
(a) Explain a monohybrid cross taking seed coat colour as a trait in Pisum sativum. Work out the cross upto F2 generation.
(b) State the laws of inheritance that can be derived from such a cross.
(c) How is the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation different in a dihybrid cross?
Frederick Griffiths experiment withStreptococcus pneumoniae (bacterium responsible for pneumonia), revealed the transforming principle of bacteria.
1. He observed two strains of this bacterium—one which formed smooth shiny colonies (S-type) with capsule, while other which formed rough colonies (R-type) without capsule.
2. When live S-type cells were injected into mice, they died due to pneumonia while when live R-type cells were injected into mice, they survived.
3. When heat-killed S-type cells were injected into mice, they survived and there were no symptoms of pneumonia observed.When, heat-killed S-type cells were mixed with live R-type cells and injected into mice, they died due to unexpected symptoms of pneumonia.
4. His experiments concluded that heat-killed S-type bacteria caused a transformation of the R-type bacteria into S-type bacteria although he was not able to understand the cause of this bacterial transformation.
OR
a. A monohybrid cross is based on the inheritance of single characters. In the case of seed coat colour as a trait in Pisum sativum the yellow colour is the dominant trait while green colour is the recessive one. In the F1progeny, all the seeds are yellow in colour which when self-crossed, give yellow and green seeds in the ratio of 3:1.
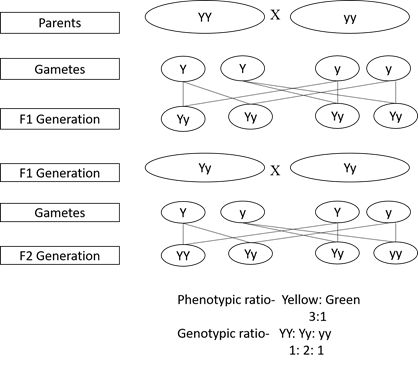
Figure 8. Monohybrid cross of seed coat color in pea.
b. The law of inheritance can be derived from such a cross:
i. Law of Dominance: This law states that in a heterozygous condition, the allele whose characters are expressed over the other allele is called the dominant allele while the other one is called recessive allele. The characters that appear in the F1 generation are called as dominant characters. The recessive characters appear in the F2 generation.
ii. Law of Segregation: According to this law, when two traits come together in one hybrid pair, the two characters do not mix with each other and are independent of each other. Each gamete receives one of the two alleles during meiosis of the chromosome.
c. Phenotypic ratio of F2 generation in monohybrid cross is 3 :1 whereas in a dihybrid cross it is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.