The market for a good is in equilibrium. How would an increase in an input price affect the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity, keeping other factors constant? Explain using a diagram.
An increase in the input price will lead to a decrease in the supply and no change in the quantity demanded.
The following figure explains how an increase in the input price would affect the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.
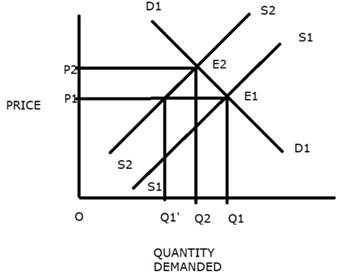
a. The market supply Falls with the increase in the input prices.
b. This leads to a leftward shift in the supply curve from S2 to S1.
c. At the initial price OP1, excess demand of q1-q1'.
d. This excess demand implies that some consumers will have to pay a higher price to purchase the extra units of output.
e. The rise in the market price will continue until it reaches OP2.
f. At OP2, the new supply curve S2 intersects the initial market demand curve D1 at E2.
g. E2 if the new equilibrium, OP2 is the new equilibrium price, and OQ2 is the new equilibrium output.
h. At the new equilibrium, the price has increased and the quantity has fallen.