Explain the income determination through the Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply approach.
● The equilibrium level of income is the point where the aggregate demand and aggregate supply are equal and will remain constant.
● If there is any diversion from this equilibrium level, the economic forces will work in a manner so that the original position is attained = AD=AS.
● This can be explained with the following diagram:
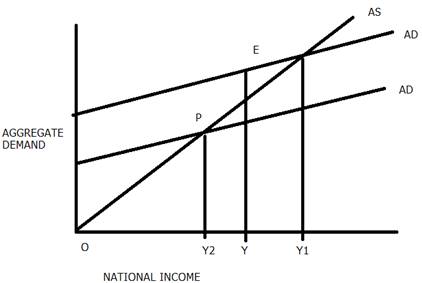
● In the above diagram, X and Y-axis represent the national income and aggregate demand.
● At point O, income = consumption. this is called breakeven point.
● The equilibrium of national income is at point E, where AD=AS.
● Let us assume that AD>AS, at Y2 and we have diverted from the original position.
● The production will have to be increased to cover up the excess demand.
● This will increase the national income, which in turn increases the consumption.
● This will continue until the AD = AS.
● Now, let us assume that again we have diverted from the original position and now AS>AS.
● There would be an unsold stock of goods piled up with the producers.
● The producer will reduce his production.
● The national income will fall and consequently, the consumption falls as well.
● This will continue till the AS=AD.