Match the species given in Column I with properties given in Column II.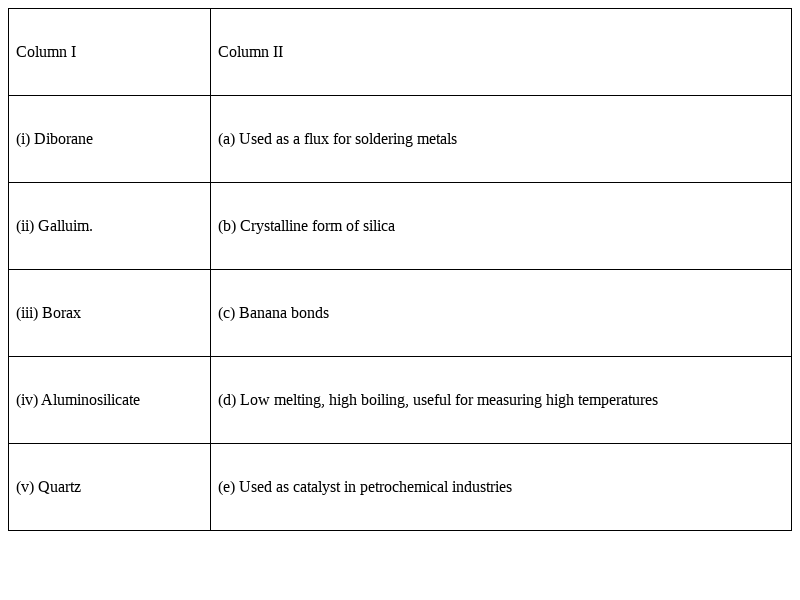
i) Diborane - (c) Banana bonds
The formation of diborane leads to the creation of new types of bonding with hydrogen atoms a) 4 terminal – 2 centered – 2 electrons and b) 2 bridging – 3 centered – 2 electrons, leading to the formation of banana bonds. In other words, in total there are 12 valence electrons, (3 ![]() from each Boron and 6
from each Boron and 6 ![]() from 6 6 H-atoms), now, out of these 4 H-atoms bind covalently with the 2 Boron atoms (8
from 6 6 H-atoms), now, out of these 4 H-atoms bind covalently with the 2 Boron atoms (8 ![]() used), while the remaining 4 electrons are shared by 2 Hydrogen – Boron atoms, form B-H-B bridge. This bridging is referred to as Banana bond.
used), while the remaining 4 electrons are shared by 2 Hydrogen – Boron atoms, form B-H-B bridge. This bridging is referred to as Banana bond.

(ii) Gallium - (d) Low melting, high boiling, useful for measuring high temperatures
Due to greater cohesive forces which held the structure together, Gallium exhibits high boiling point while its melting point is low. Therefore, used to measure high temperatures.
(iii) Borax - (a) Used as a flux for soldering metals
Borax is used for soldering metals. Borax is used
along with ![]() (flux) for welding purposes. Sometimes, it is also
(flux) for welding purposes. Sometimes, it is also
mixed with water to solder jewellery and gold.As, it lowers the
melting pointand allows themolten mixture to flow easily in the
shapes. Thus, helps used in soldering.
(iv) Aluminosilicate - (e) Used as catalyst in petrochemical industries
Aluminosilicate is a compound which is composed of Aluminium and Silicon mainly, also called as Zeolites. Nowadays, aluminosilicates are commonly used in petrochemical industries as a catalyst used to synthesis ethylene and propene. These are the compounds which can accelerates the chemical reactions, called as catalysts. They are usually used in the preparation of gasoline from crude oil and in the petrochemical industries for cracking of hydrocarbons.
(v) Quartz - (b) Crystalline form of silica
Quartz is composed up of elements - Si and Oxygen and having formula ![]() . It is a crystalline structure formed by the joining of repeating units of
. It is a crystalline structure formed by the joining of repeating units of![]() . It is available in several colorsand varieties. They used in jewellery making and stone carving.
. It is available in several colorsand varieties. They used in jewellery making and stone carving.

(a part showing crystalline form of Quartz)