A long, straight wire carrying a current of 1.0 A is placed horizontally in a uniform magnetic field B = 1.0 × 10–8 T pointing vertically upward figure. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at the points P and Q, both situated at a distance of 2.0 cm from the wire in the same horizontal plane.
Given :
Current in the wire : i = 1.0 A
Magnitude of Horizontal magnetic field: Bo = 1.0 × 10–5 T
Distance between points P,Q and the wire :
d = 2.0 cm = 0.02 m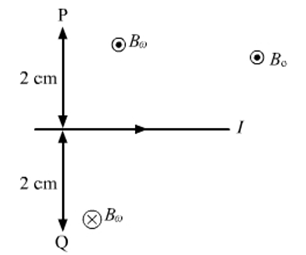
Right hand rule is used to determine the direction of the magnetic field due to the current carrying wire. Cross determines the field going into the plane and dot determines the field coming out of the field.
Bw is the magnetic field due to wire.
Formula used:
By Ampere’s Law for a current carrying wire is![]() Where,
Where,
B is the magnitude of magnetic field,
μ0 is the permeability of free space, μ0= 4π × 10-7 T mA-1
d is the distance between the current carrying wire and the required point.
Magnetic field at point P due to wire,![]()
![]()
Resultant magnetic field at P
BP = Bo +Bw
∴ BP = 1× 10-5 + 1× 10-5
∴ BP = 2 × 10-5 T
Magnetic field at point Q due to wire,![]()
![]() ∴ Bw = - 1 × 10-5 T
∴ Bw = - 1 × 10-5 T
The negative sign is because the field at Q is opposite to the direction of horizontal field and at P.
Resultant magnetic field at P
BQ = Bo +Bw
∴ BQ = 1× 10-5 - 1× 10-5
∴ BQ = 0
Hence, resultant magnetic field at P is 2 × 10-5 T and at Q is 0.