The X-ray beam coming from an X-ray tube
The wavelength of X-ray photon is given by: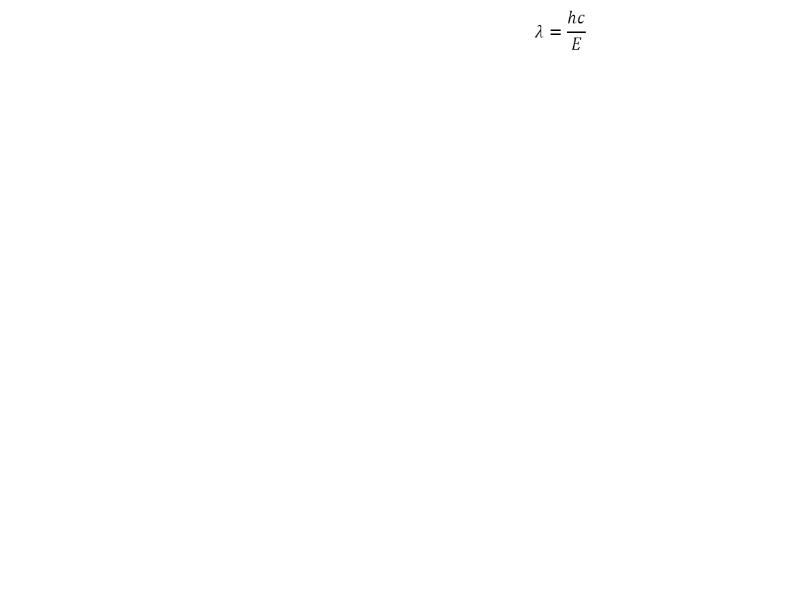
Here, λ is the wavelength of light, h is the Planck’s constant (6.62607004 × 10-34 m2 kg / s), and c is the speed of light in vacuum and E” is the energy of the electron which can range from 0”to eV
![]()
And the minimum wavelength that the photon can have is
where, “eV” is the kinetic energy acquired by the electron. So, in principle, x-rays can have any wavelength greater than the cut-off wavelength.
1