A rectangular conducting loop consists of two wires on two opposite sides of length l joined together by rods of length d. The wires are each of the same material but with cross-sections differing by a factor of 2. The thicker wire has a resistance R and the rods are of low resistance, which in turn are connected to a constant voltage source V0. The loop is placed in uniform a magnetic field B at 45° to its plane. Find τ, the torque exerted by the magnetic field on the loop about an axis through the centres of rods.
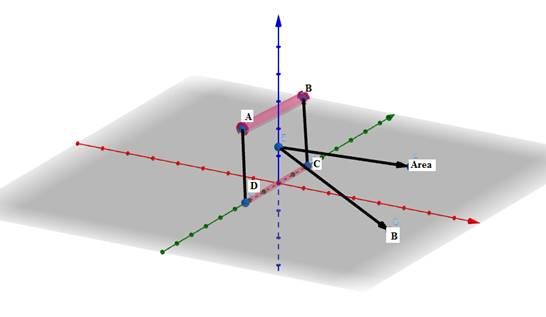
The cross section of AB is twice that of CD.
As they are made of same material, they are going to have same resistivity. Hence, the resistances are;
![]()
![]()
i.e. RAB = 2 R and RCD = R
Now, let us calculate the force (as direction can be assumed we only concentrate on the magnitude),
![]()
The torque is going to be ![]()
![]()


Similarly, we can find for CD

The net torque is going to be,
![]()


![]()