(a) Draw the graph between vapour pressure and temperature andexplain the elevation in boiling point of a solvent in solution.
(b) Determine the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by
dissolving 25 mg of K2SO4 in 2 litres of water at 25°C assuming it to be completely dissociated. (Atomic masses K = 39 u, S = 32 u, O = 16 u)
OR
(a) Write two characteristics of non-ideal solution.
(b) 2 g of benzoic (C6H5COOH) dissolved in 25 g of benzene shows a depression in freezing point equal to 1.62 K. Molal depression constant for benzene is 4.9 K kg mol–1. What is the percentage association of acid if it forms dimer in solution ?
(a) 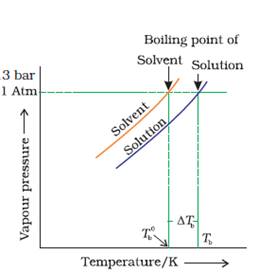
When a solute is added to a solvent, the vapour pressure of the solvent decreases and at higher temperatures, it becomes equal to atmospheric pressure.
Boiling point elevation occurs whenever a non-volatile solute is added to a pure solvent.
This phenomenon occurs when the boiling point of the solvent is increased when another compound, a solute is added, such that the solution, so formed has a higher boiling point than the pure solvent.
rTb = Kb × m
Where rTb the elevation in boiling point,
Kb is the molal boiling point elevation constant,
m is the molality of solute.
(b) K2SO4 dissociates as:
![]()
Total ions produced (n) = 2+1 = 3
C = molarity of solute = ![]()
Molecular mass = 2×39 + 32 + 16×4 = 174 gm
Mass given = 25mg = 0.025gm
Moles = ![]()
Volume in L = 2L
∴ C =![]() [M]
[M]
R, ideal gas constant = 0.0821L atm mol-1K-1.
Temperature T = 25° C = (25+273)K = 298K
Osmotic pressure π = n × C × R × T
= (3 × ![]() × 0.0821 × 298)atm
× 0.0821 × 298)atm
=5.27×10-3 atm.
Therefore, osmotic pressure is 5.27×10-3 atm.
OR
(a) Some characteristics of non-ideal solution:
(i)Volume change of mixing should not be zero.
(ii)Heat change on mixing should not be zero.
(iii)Solute molecules dissociate in the ideal solution.
(iv)Solute molecules associate in the ideal solution.
(v)Ideal solutions must not obey Raoult’s law at all concentrations.
Eg.Mixture of acetone and chloroform.
(b) rTf = i× Kf × m
Where rTfthe depression in freezing point = 1.62 K
i is the Vant-Hoff factor
Kf is the molal freezing point depression constant = 4.9 K kg mol–1.
m is the molality of solute.
As the acid dimerises, N = 2
Molar mass of CH3COOH = 61gm, when it dimerises, it becomes (2×61)gm = 122gm.
Moles of acid (solute) = 2/122
Weight of solvent in kg = 0.025kg.
So, m = ![]() =0.656
=0.656
Thus, i = ![]() =0.504
=0.504
Degree of association α = N(1-i)
Replacing the value of N=2 and i = 0.504, we get:
α = 2(1-0.504) = 0.992 = (0.992×100)% = 99.2%
So, 99.2% association.