[CoF6]3- and [Co(en)3]3+, which one complex is:
(i) Paramagnetic
(ii) More stable
(iii) Inner orbit complex and
(iv) High spin complex
(atomic no. of Co = 27)
Hybridization of [CoF6]3-
Co3+ is the central atom with a fluoride ligand being the donor.
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 7
= 4s2, 3d7
Oxidised state = 4s0, 3d6
Orbital of Co3+
![]() Since (F) is a weak field ligand according to the spectrochemical series of ligands it acquires higher energy orbitals and thus results in no spin pairing of electrons in the lower d orbital and acquires one empty s orbital, three p orbitals and two empty d orbitals of higher energy, to give sp3d2 hybridization.
Since (F) is a weak field ligand according to the spectrochemical series of ligands it acquires higher energy orbitals and thus results in no spin pairing of electrons in the lower d orbital and acquires one empty s orbital, three p orbitals and two empty d orbitals of higher energy, to give sp3d2 hybridization.
Orbital of Co3+ undergoing hybridization
The given structure shows sp3d2 hybridization, and as the compound has 3 unpaired electrons it is paramagnetic.
Due to acquiring of higher energy orbitals the stability of the compound decreases significantly.
Also the outer d-orbitals are used for bonding thus the compound is outer complex and is a high spin complex.
Hybridization of [CoF6]3-
Co3+ is the central atom with a fluoride ligand being the donor.
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 7
= 4s2, 3d7
![]()
Oxidised state = 4s0, 3d6
Orbital of Co3+
Since (en) is a strong field ligand according to the spectrochemical series of ligands it acquires lower energy orbitals and thus results in spin pairing of electrons in the lower d orbital and acquires one empty s orbital, three p orbitals and two empty d orbitals of lower energy, to give d2sp3d2 hybridization.
Orbital of Co3+ undergoing hybridization
![]()
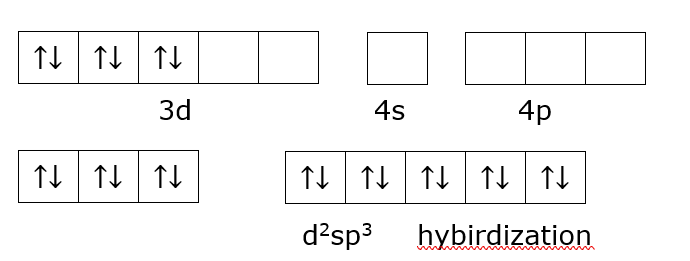
d2sp3 hybirdization
The given structure shows d2sp3 hybridization, and as the compound has 0 unpaired electrons it is diamagnetic.
Due to acquiring of lower energy orbitals the stability of the compound increases significantly.
Also the inner d-orbitals are used for bonding thus the compound is inner complex and is also a low spin complex.