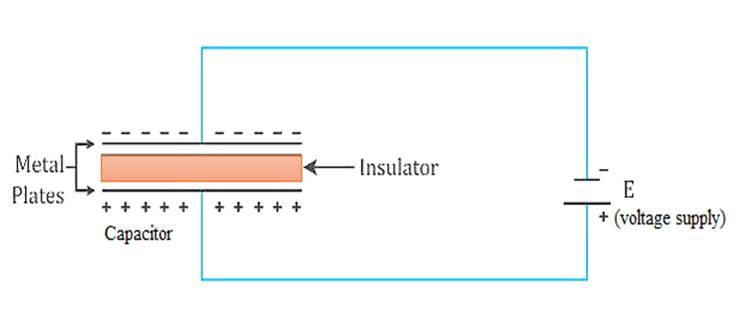
Explain briefly the process of charging a parallel plate capacitor when it is connected across a d.c. battery.
A capacitor of capacitance ‘C’ is charged to ‘V’ volts by a battery. After some time, the battery is disconnected and the distance between the plates is doubled. Now a slab of dielectric constant, 1 < k < 2, is introduced to fill the space between the plates. How will the following be affected: (a) The electric field between the plates of the capacitor
(b) The energy stored in the capacitor
Justify your answer by writing the necessary expressions.
Consider a parallel plate capacitor connected across a d.c. voltage supply as shown in the figure. When the circuit is closed, the electric current will flow through it. As the charges reaches to the plate, the insulating gap does not allow the charges to move further; hence, positive charges get deposited on one side of the plate and negative charges get deposited on the other side of the plate. When the voltage starts to develop, the electric charge begins to resist the deposition of further charge. Thus, the current flowing through the circuit gradually becomes less and then zero till the voltage of the capacitor is exactly equal but opposite to the voltage of the battery. This is how the capacitor gets charged when it is connected across a d.c. battery.
(a) The electric field between the plates is
![]()
The distance between plates is doubled, d' = 2d
![]()
Therefore, when the distance between the plates is double, the electric field will reduce
to one half.
(b) As the capacitance of the capacitor,
![]()
Energy stored in the capacitor is ![]()
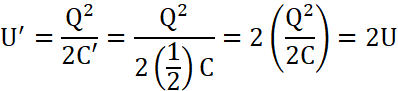
Therefore, when the distance between the plates is doubled, the capacitance reduces to half. Therefore, energy stored in the capacitor becomes double.