(a) With the help of labelled ray diagram show the path followed by a narrow beam of monochromatic light when it passes through a glass prism.
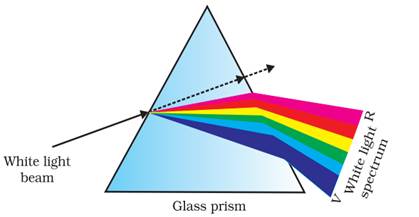
(b) What would happen if this beam is replaced by a narrow beam of white light ?
OR
(a) A person is suffering from both myopia and hypermetropia.
(i) What kind of lenses can correct this defect ?
(ii) How are these lenses prepared ?
(b) A person needs a lens of power + 3D for correcting his near vision and – 3D for correcting his distant vision. Calculate the focal lengths of the lenses required to correct these defects.
(a) In the case of monochromatic light the ray will bend due to refraction but it will not show dispersion of light.
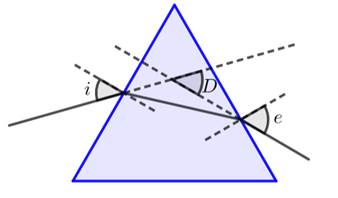
(b) When a white beam of light is allowed to pass through the prism, it will get dispersed into its 7 color component of spectrum of light. The splitting of light into its component colours is called dispersion.
The following diagram show the phenomena: -
OR
(a) (i) A person suffering from both myopia and hypermetropia at the same time requires a spectacle consisting of both concave and convex lens of prescribed focal length.
(ii) It is prepared by setting half the lens of the spectacle to be concave and the remainder half to be a convex type lens.
(b) The power of the lens is defined as the reciprocal of the focal length. It is a measure of the ability of the lens to focus.
Mathematically, it can be described as,
![]()
The power of the lens is + 3 D
![]()
![]()
The power of the lens is - 3 D
![]()
![]()