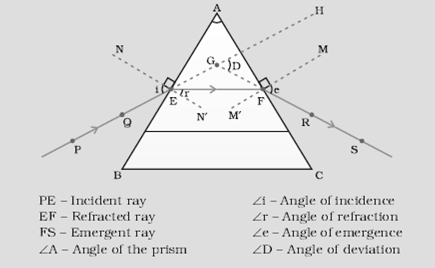
Explain the refraction of light through a triangular glass prism using a labelled ray diagram. Hence define the angle of deviation.
Let PE is the incident light on the prism, EF is the refracted ray and FS is the emergent ray. When a ray of light is entered through surface AB from air to glass, then the light ray suffer refraction and bend towards the normal ray. At the second surface AC, the rays enter from glass to air which results in bending away from the normal ray. The angle of incidence and the angle of refraction are equal. The emergent ray bend at an angle towards the direction of incident ray. This angle is known as Angle of deviation.
It can be shown with the following ray diagram:
27