Given on the next page is a simple diagram o circulation of blood in a mammal showing the blood vessels, the heart, lungs and body tissues. The blood vessel, labelled 6, contains deoxygenated blood and the valve leading to it has three semi-lunar pockets.

(a) Name the blood vessels and organs marked by numbers 1 to 8.
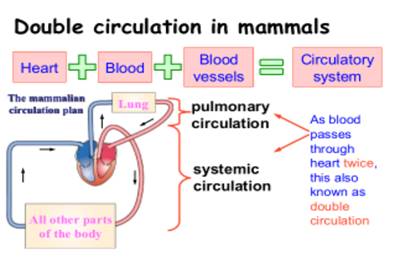
(b) What is meant by the term 'double circulation' of blood in mammals?
(c) What is diastole?
(a) The blood vessels and organs marked by numbers 1 to 8 are in the figure are as shown below:
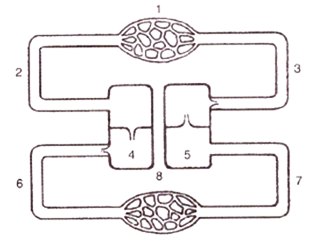
1: Body tissues (it includes all the visceral organs which are bathed in blood)
2 : Venacava (as it is carrying blood from body tissues to right auricle)
3 : Aorta (as it is carrying blood away from He ( art to other body parts)
4 : Right ventricle (as pulmonary artery arises from the right ventricle)
5 : Left auricle as pulmonary vein is arising from lungs to left auricle)
6 : Pulmonary artery (as it is carrying blood from right ventricle to the lungs)
7 : Pulmonary vein (as it is carrying blood from lungs to the left auricle)
8 : Lungs (as pulmonary artery is draining de oxygenated blood into lungs and pulmonary vein is carrying oxygenated blood to the left auricle).
(b) Double circulation of blood means blood flows twice in the heart before it completes one full round :
The short pulmonary circulation (from right ventricle through pulmonary artery to lungs & back through pulmonary veins into left auricle).
The long systemic circulation (from left ventricle through aorta & back to right auricle through superior & inferior venacava).
(c) The relaxing or expansion phase of the heart during cardiac cycle is called diastole.
During ventricular diastole blood enters ventricle by crossing through tricuspid & bicuspid valve. During Atrial diastole , blood passes into aorta & pulmonary artery through semilunar valves.