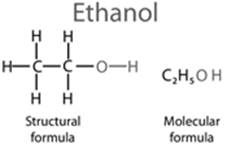
Define a homologues series. Give the name and structural formula of one homologues of the following:
CH3OH
A series of organic compounds in which hydrogen in a carbon chain is replaced by the same functional group, is called homologous series. Any two adjacent homologues differ by (-CH2) in their molecular formulae.
Ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) is a successive homologous of methyl alcohol (CH3OH). The IUPAC name of ethyl alcohol is ethanol.
33