Show that f : [–1, 1] → R, given by 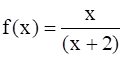 is one-one. Find the inverse of the function f : [–1, 1] → Range f.
is one-one. Find the inverse of the function f : [–1, 1] → Range f.
(Hint: For y ∈ Range f, y = 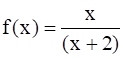 , for some x in [–1, 1], i.e.,
, for some x in [–1, 1], i.e., 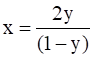 )
)
It is given that f : [–1, 1] → R, given by 
Now, Let f(x) = f(y)

⇒ xy + 2x = xy +2y
⇒ 2x = 2y
⇒ x = y
⇒ f is a one- one function.
Now, Let y =  , xy = x + 2y so x =
, xy = x + 2y so x = 
So, for every y in the range there exists x in the domain such that f(x) = y
⇒ f is onto function.
⇒ f: [-1,1] → Range f is one-one and onto
⇒ the inverse of the function : f: [-1, 1] → Range f exists.
Let g: Range f → [-1, 1]be the inverse of range f.
Let y be an arbitrary element of range f.
Since, f :[-1, 1] → Range f is onto, we get:
y = f(x) for same x ϵ [-1, 1]

⇒ xy +2y = x
⇒ x(1 - y) = 2y
⇒ x =  , y ≠ 1
, y ≠ 1
Now, Let us define g: Range f → [-1, 1]
g(y) =  , y ≠ 1
, y ≠ 1
Now, (gof)(x) = g(f(x)) = 
(fog)(y) = f(g(y)) = 
Thus, gof = I[-1,1] and fog = IRange f
⇒ f-1 = g
Therefore, f-1(y) =  , y ≠ 1
, y ≠ 1