The first (∆iH1) and the second(∆iH2) ionization enthalpies (in kJ mol–1) and the ![]() electron gain enthalpy (in kJ mol–1) of a few elements are given below:
electron gain enthalpy (in kJ mol–1) of a few elements are given below:
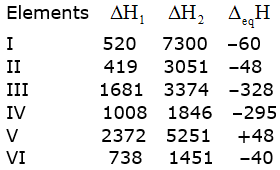
Which of the above elements is likely to be?
A. the least reactive element.
B. the most reactive metal.
C. the most reactive non-metal.
D. the least reactive non-metal.
E. the metal which can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX2(X=halogen).
F. the metal which can form a predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX (X=halogen)?
(A.) Element V is likely to be the least reactive element. This is because it has the highest first ionization enthalpy (∆H1) and a positive electron gain enthalpy (∆egH).
(B.) Element II is likely to be the most reactive metal as it has the lowest first ionization enthalpy (∆H1) and a low negative electron gain enthalpy (∆egH).
(C.) Element III is likely to be the most reactive non–metal as it has a high first ionization enthalpy (∆H1) and the highest negative electron gain enthalpy (∆egH).
(D.) Element V is likely to be the least reactive non–metal since it has a very high first ionization enthalpy (∆H2) and a positive electron gain enthalpy (∆egH).
(E.) Element VI has a low negative electron gain enthalpy (∆egH). Thus, it is a metal. Further, it has the lowest second ionization enthalpy (∆H2). Hence, it can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX2(X=halogen).
(F.) Element I have low first ionization energy and high second ionization energy. Therefore, it can form a predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX (X=halogen).