Derive equations of motion by graphical method.
Derivation of equations by graphical method.
Equations of motion from velocity-time graph:
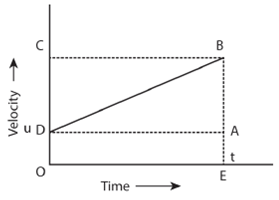
The graph shows the change in velocity with time for a uniformly accelerated object. The object starts from the point D in the graph with velocity u. Its velocity keeps increasing and after time t it reaches the point B on the graph.
The initial velocity of the object = u = OD = EA
The final velocity of the object = v = OC = EB
Time = t = OE = DA
Also from the graph we know that, AB = DC
First equation of motion
By definition, acceleration 




DC = AB = at
From the graph EB = EA + AB
v = u + at
This is the first equation of motion
Second equation of motion
From the graph, the distance covered by the object during time t is given by the area of quadrangle DOEB
s = area of the quadrangle DOEB
= area of the rectangle DOEA + area of the triangle DAB
= (AE × OE) + (1/2× AB × DA)
s = ![]()
This is the second equation of motion.
The third equation of motion
From the graph, the distance covered by the object during time t is given by the area of the quadrangle DOEB.
Here DOEB is a trapezium.
Then,
S = area of trapezium DOEB
= 1/2 × sum of length of parallel side × distance between parallel sides
= 1/2 × (OD + BE) × OE
= ![]()
since ![]()

Therefore ![]()
![]()