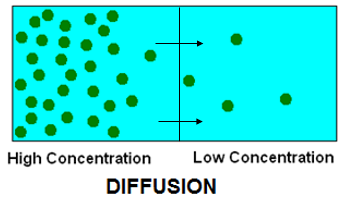
Define diffusion and explain the rate of the order of diffusion in solids, liquids, and gases.
Diffusion is an essential means of transport in plants. It refers to the movement of substances along the concentration gradient (from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration). It is a slow process which takes place through a semi-permeable membrane.
Example – the aroma of an incense stick diffuses quickly through the air.
Rate of diffusion
The rate of diffusion depends on a few factors such as temperature, pressure, membrane permeability and concentration of gradient.
The rate of diffusion is fastest in gases and slowest in solids. This is because in solids molecules are very tightly packed and in gases molecules are very loosely packed.