Solve the following system of the linear equations by Cramer’s rule:
6x + y – 3z = 5
X + 3y – 2z = 5
2x + y + 4z = 8
Given: - Equations are: –
6x + y – 3z = 5
X + 3y – 2z = 5
2x + y + 4z = 8
Tip: - Theorem – Cramer’s Rule
Let there be a system of n simultaneous linear equations and with n unknown given by
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
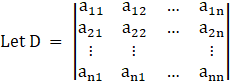
and let Dj be the determinant obtained from D after replacing the jth column by
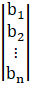
Then,
![]() provided that D ≠ 0
provided that D ≠ 0
Now, here we have
6x + y – 3z = 5
x + 3y – 2z = 5
2x + y + 4z = 8
So by comparing with theorem, lets find D , D1 and D2
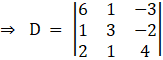
Solving determinant, expanding along 1st Row
⇒ D = 6[(4)(3) – (1)( – 2)] – 1[(4)(1) + 4] – 3[1 – 3(2)]
⇒ D = 6[12 + 2] – [8] – 3[ – 5]
⇒ D = 84 – 8 + 15
⇒ D = 91
Again, Solve D1 formed by replacing 1st column by B matrices
Here
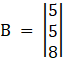
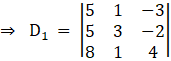
Solving determinant, expanding along 1st Row
⇒ D1 = 5[(4)(3) – ( – 2)(1)] – 1[(5)(4) – ( – 2)(8)] – 3[(5) – (3)(8)]
⇒ D1 = 5[12 + 2] – 1[20 + 16] – 3[5 – 24]
⇒ D1 = 5[14] – 36 – 3( – 19)
⇒ D1 = 70 – 36 + 57
⇒ D1 = 91
Again, Solve D2 formed by replacing 1st column by B matrices
Here
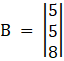
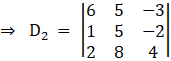
Solving determinant
⇒ D2 = 6[20 + 16] – 5[4 – 2( – 2)] + ( – 3)[8 – 10]
⇒ D2 = 6[36] – 5(8) + ( – 3)( – 2)
⇒ D2 = 182
And, Solve D3 formed by replacing 1st column by B matrices
Here
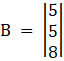
⇒ 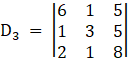
Solving determinant, expanding along 1st Row
⇒ D3 = 6[24 – 5] – 1[8 – 10] + 5[1 – 6]
⇒ D3 = 6[19] – 1( – 2) + 5( – 5)
⇒ D3 = 114 + 2 – 25
⇒ D3 = 91
Thus by Cramer’s Rule, we have
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ x = 1
again,
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ y = 2
and,
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ z = 1