Evaluate the following limits:

As we need to find ![]()
We can directly find the limiting value of a function by putting the value of the variable at which the limiting value is asked if it does not take any indeterminate form (0/0 or ∞/∞ or ∞-∞, .. etc.)
Let Z = ![]()
∴ We need to take steps to remove this form so that we can get a finite value.
TIP: Most of the problems of logarithmic and exponential limits are solved using the formula![]() and
and ![]()
It also involves a trigonometric term, so there is a possibility of application of Sandwich theorem- ![]()
As Z = ![]()
To apply the formula we need to get the form as present in the formula. So we proceed as follows-
∵ Z = ![]()
Multiplying numerator and denominator by √(1+cos x)
⇒ Z = ![]()
Using (a+b)(a-b) = a2-b2
Z = ![]()
∵ √(1-cos2x) = sin x
⇒ Z = ![]()
{using algebra of limits}
⇒ Z = ![]()
Dividing numerator and denominator by x-
Z = 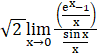
⇒ Z = 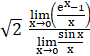
Use the formula: ![]() and
and ![]()
∴ Z = ![]()
{∵ log e = 1}
Hence,
![]()