(a) An electric dipole is kept first to the left and then to the right of a negatively charged infinite plane sheet having a uniform surface charge density. The arrows P1 and P2 show the directions of its electric dipole moment in the two cases.

Identify for each case, whether the dipole is in stable or unstable equilibrium. Justify each answer.
(b) Next, the dipole is kept in a similar way (as shown), near an infinitely long straight wire having uniform negative linear charge density.

Will the dipole be in equilibrium at these two positions? Justify your answer.
a) As for a negatively charged infinite plane sheet having a uniform surface charge density the value of electric field is
![]()
Which is independent of the distance from the sheet so the dipole will be in stable equilibrium whether it is kept first to the left and then to the right.
b) The value of electric field for an infinitely long straight wire having uniform negative linear charge density λ is given as,
![]()
Where r is the distance from the line charge.
As the value of electric field near the vicinity of the wire depends upon r the dipole will not be in stable equilibrium whetherits direction is towards the wire or away from it.
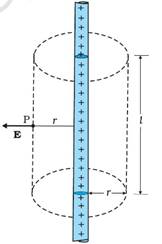
Note:
The electric field due an infinite line charge is derived using the Gauss’s law,
Flux through the Gaussian surfaces shown in the diagram aside
= flux through the curved cylindrical part of the surface
= E × 2 πrl
The surface includes charge equal to λ l. Gauss’s law then gives
![]()
![]()