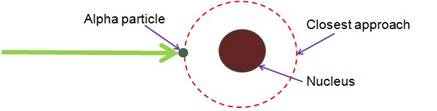
Define the distance of closest approach. An α-particle of kinetic
energy ‘K’ is bombarded on a thin gold foil. The distance of the closest
approach is ‘r’. What will be the distance of closest approach for an
α-particle of double the kinetic energy?
OR
Write two important limitations of Rutherford nuclear model of
atom.
The distance of the closest approach is defined as the minimum distance of the charged particle from the nucleus at which initial kinetic energy is the same to the potential energy of the nucleus.
This distance (r) isknown as distance of closest approach.
K.E=P.E
From the given data kinetic energy,
![]() -- > (1)
-- > (1)
Where,
ϵ0 = permittivity of the space
e = charge of electron
r = distance
Z = mass number
Solving for r, we get
![]()
if k is doubled than let, r0 be the new distance.
Then we have,
![]() -- > (2)
-- > (2)
Solving for r’, we get
![]()
Dividing equation 2 by 1,
![]()
![]()
OR
Rutherford’s atomic model also called as planetary model can be
represent like the following diagram with the circular orbits in which
electrons are orbiting around the nucleus.

1. A revolving electron should emit radiation because of force on it. This leads to decrease in energy of the electron. So, concept of circular orbit is not valid.
2. Rutherford’s atomic model can’t explain the arrangement of the electrons in the atom